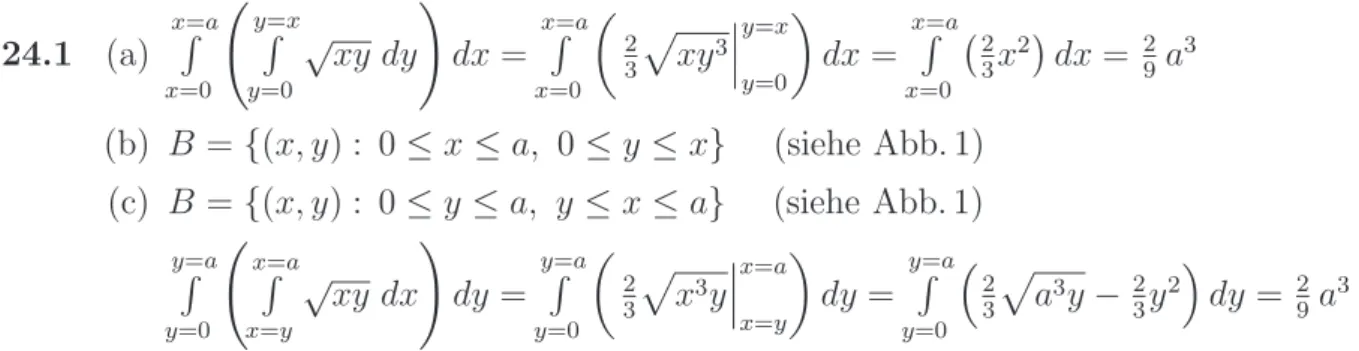L¨ osungen zur 24. ¨ Ubung
H¨ohere Mathematik II (MB)
24.1 (a)
x=a
R
x=0 y=x
R
y=0
√xy dy
! dx=
x=a
R
x=0
2 3
pxy3
y=x y=0
dx=
x=a
R
x=0 2 3x2
dx= 29a3 (b) B ={(x, y) : 0 ≤x≤a, 0≤y≤x} (siehe Abb. 1)
(c) B ={(x, y) : 0 ≤y ≤a, y≤x≤a} (siehe Abb. 1)
y=a
R
y=0 x=a
R
x=y
√xy dx
! dy =
y=a
R
y=0
2 3
px3y
x=a x=y
dy =
y=a
R
y=0
2 3
pa3y−23y2
dy= 29a3
24.2 Entsprechend der Integrationsgrenzen hat der Normalbereich die Darstellung B ={(x, y) : −2≤y≤0, y2−4≤x≤0}
bzw. alternativ
B ={(x, y) : −4≤x≤0, −√
x+ 4 ≤y ≤0} (siehe Abb. 1).
Hieraus findet man das Doppelintegral mit vertauschter Integrationsreihenfolge:
x=0
R
x=−4
y=0
R
y=−
√x+4
y3 dy
! dx =
x=0
R
x=−4
1 4y4
y=0 y=−
√x+4
dx=
x=0
R
x=−4
−14(x+ 4)2dx=−163
(-4,0)
(0,-2) (a,0)
(a,a)
Abbildung 1: Aufgaben 1 und 2
24.3 (a) B ={(x, y) : 2 ≤x ≤4, 4x ≤y≤x} RR
B
y db =
4
R
2 x
R
4/x
y dy
! dx=
4
R
2
1 2y2
x 4/x
dx=
4
R
2 1 2x2− 12
16 x2
dx= 223 (b) B ={(x, y) : −1≤y≤0, y+ 1 ≤x≤ey}
RR
B
y2 db =
0
R
y=−1 ey
R
x=y+1
y2 dx
!
dy = 2312 −5e−1 ≈0.07727
24.4 A= Z Z
B
1 db =
2
Z
0
√8x
Z
0
1dy dx = 16 3 ,
Z Z
B
x db = 32 5 ,
Z Z
B
y db = 8
Die Schwerpunktskoordinaten sind xS = 1 A
Z Z
B
x db , yS = 1 A
Z Z
B
y db ,
also ist S(1.2,1.5) der geometrische Schwerpunkt von B.
Rotation vonB ={(x, y) : 0 ≤x≤2, 0≤y≤√
8x} um die Gerade y = 0 : Volumen des Rotationsk¨orpers: V =πR2
0
√8x2
dx = 16π Fl¨ache von B: A= 163
Umfang des erzeugten Kreises: U = 2πyS = 3π, also gilt V =A·U. Rotation vonB um die Gerade x= 2 :
Volumen des Rotationsk¨orpers: V =πR4
0
2− y82
2
dy = 12815π Fl¨ache von B: A= 163
Umfang des erzeugten Kreises: U = 2π(2−xS) = 85π, also gilt V =A·U. 24.5 (a) r¨aumlicher Normalbereich
B ={(x, y, z) : 0 ≤x≤4, 0≤y≤4−x, 0≤z ≤x2 +y2} V =
4
Z
0 4−x
Z
0
x2+y2
Z
0
1dz dy dx=
4
Z
0 4−x
Z
0
(x2+y2)dy dx= 128 3 (b) r¨aumlicher Normalbereich
B ={(x, y, z) : 1 ≤x2+y2 ≤4, 0≤z≤x+ 2} Ubergang zu Zylinderkoordinaten:¨
B ={(r, ϕ, z) : 1≤r ≤2, 0≤ϕ≤2π, 0≤z ≤x+ 2 =rcosϕ+ 2} V =
2
Z
r=1 2π
Z
ϕ=0
rcosϕ+2
Z
z=0
r dz dϕ dr=
2
Z
r=1 2π
Z
ϕ=0
(rcosϕ+ 2)r dϕ dr= 6π ≈18.85
24.6 (a) V = Z Z Z
B
1 db =
1
Z
0 x
Z
0
x+3y+1
Z
0
dz dy dx= 4 3 (b)
Z Z Z
B
x db = 23
24, d.h. xS = 23
32 = 0.719, Z Z Z
B
y db = 13
24, d.h. yS = 13
32 = 0.406, Z Z Z
B
z db = 47
24, d.h. zS = 47
32 = 1.469
Aufgaben und L¨osungen im Web : www.tu-chemnitz.de/∼ustreit
Bemerkungen an : u.streit@mathematik.tu-chemnitz.de [31. Mai 2019]