ζ . Kristallogr. NCS 213 (1998) 4 6 7 ^ 6 8
467
© by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, München
Crystal structure of thulium pentaphosphide, TmPs and of lutetium pentaphosphide, LuPs
H. G. von Schnering, M. Wittmann and K. Peters
Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung. Heisenbergstraße 1, D-70569 Stuttgart. Germany
Received December 17. 1997. transferred to 2nd update of database ICSD in 1998, CSD-No. 409186 and CSD-No. 409187
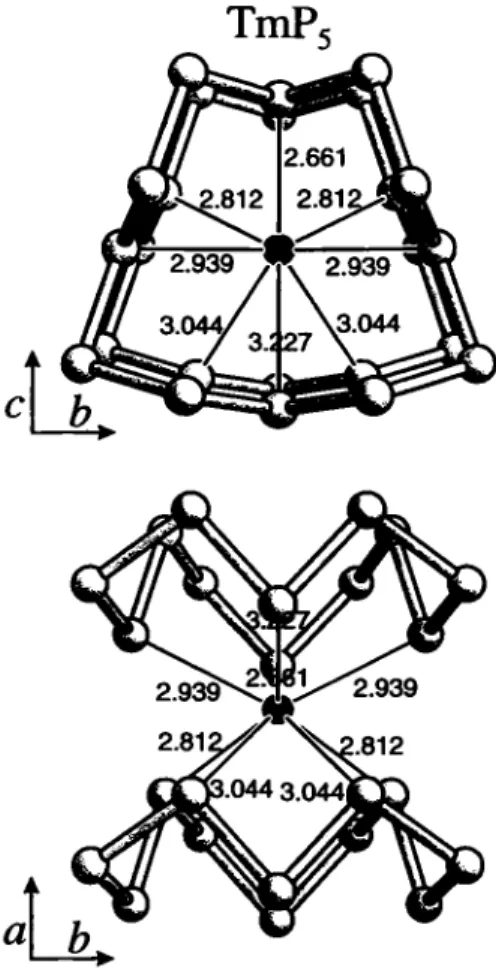
TmP. 1. Thulium pentaphosphide, TinPs
Source of material: The compound was formed by reaction of the elements in a sealed glass ampoule at 783 К (2 weeks) in the presence of molten LiCl/KJ and a small amount of iodine (see ref 1). TmPs forms bright black crystals of prismatic or columnar shape and is stable against dilute bases and non-oxidizing acids.
The compound is paramagnetic with Цсгг = 7.6 ць (see réf. 2).
TmPs crystallizes in the space group P2 \lm and is isotypic to NdPs (see ref. 3). The distances vary between 2.158 Â and 2.209 Â for P - P and between 2.661 Â and 3.227 Â for Tm-P.
PsTm, monoclinic,/>12i/ml (No. 11), a =4.876(1) Â, b =93X1(2) Â, с =5.299(1) К ß=102J5(3)°, V=235.2Â^ Ζ =2, ÄfF) =0.070, Ry^F) =0.076.
Table 1. Parameters used for the X-ray data collection Crystal: black, spherical, metallic luster.
size 0.1 mm
Wavelength: Mo Ka radiation (0.71073 Л)
μ:
203.6 cm"'EMfiiractometer: SYNTEXPl
Scan mode:
ω
Tmeasunmenl'· 293 К
2θ™χ: 55°
щтшш,··'·
609Criterion for Io. / „ > 2 σ ( / ο ) ìi{param)relmedr· 31
Program: SHELXTL-plus
Table 2. Final atomic coordinates and displacement parameters (in Â^)
Atom Site X
У
ζUn
ί/22 ί/ззUn Un Uli
Tm
2e
0.0048(2) 1/4 0.3993(2) 0.0124(6) 0.0100(6) 0.0105(6) 0 0.0014(4) 0P(l) 4 / 0.3817(8) 0.5926(4) 0.0423(7) 0.013(1) 0.010(2) 0.012(2) 0.002(2) 0.002(1) -0.001(1) P(2) 4 / 0.2831(8) 0.5298(5) 0.4044(7) 0.016(2) 0.011(2) 0.014(2) 0.001(1) 0.005(1)
ο.ω2(ΐ)
P(3)
2e
0.273(1) 1/4 0.894(1) 0.012(2) 0.014(2) 0.015(2) 0 0.002(2) 0468
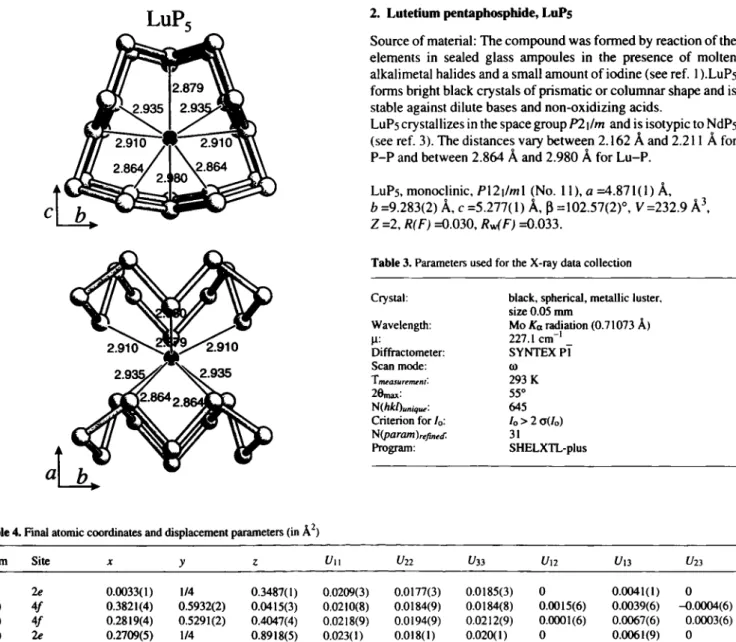
TmPs and LuPsLuP. 2. Lutetium pentaphosphide, LuPs
Source o f material: T h e c o m p o u n d w a s f o r m e d by reaction o f the e l e m e n t s in sealed glass a m p o u l e s in the p r e s e n c e o f molten alkalimetal halides and a small amount o f iodine ( s e e r e f 1 ).LuP5 forms bright black crystals o f prismatic or c o l u m n a r shape and is stable against dilute bases and n o n - o x i d i z i n g acids.
LuPs crystallizes in the space group P 2 i / m and is isotypic to N d P s ( s e e ref. 3). The distances vary b e t w e e n 2 . 1 6 2 Â and 2.211 À for P - P and between 2 . 8 6 4 À and 2 . 9 8 0 Â for L u - P .
LuPs, monoclinic, />12 i/m 1 ( N o . 11 ), α = 4 . 8 7 1 ( 1 ) Â , b = 9 . 2 8 3 ( 2 ) Â, с = 5 . 2 7 7 ( 1 ) Â, β = 1 0 2 . 5 7 ( 2 ) ° , V = 2 3 2 . 9 Â ^ Ζ = 2 , R(F) = 0 . 0 3 0 , R ^ F } = 0 . 0 3 3 .
Table 3. Parameters used for the X-ray data collection
Crystal: black, spherical, metallic luster.
size 0.05 mm
Wavelength: Mo Ka radiauon (0.71073 Â)
μ: 227.1 cm"'
Diffractometer: SYNTEX PI
Scan mode: ω
Tmeasurement'. 293 К
20inax: 55°
^hkDumque·. 645
Criterion for lo: / ο > 2 σ ( / ο )
ti{paratn)refiníd·. 31
Program: SHELXTL-plus
Table 4. Final atomic coordinates and displacement parameters (in Â^)
Atom Site X У ζ t/ll U21 t/33 t/12 U l i Í/23
Lu 2e 0.0033(1) 1/4 0.3487(1) 0.0209(3) 0.0177(3) 0.0185(3) 0 0.0041(1) 0
P(l) 4 / 0.3821(4) 0.5932(2) 0.0415(3) 0,0210(8) 0.0184(9) 0.0184(8) 0.0015(6) 0.0039(6) -0.0004(6) P(2) 4 / 0.2819(4) 0.5291(2) 0.4047(4) 0.0218(9) 0.0194(9) 0.0212(9) 0.0001(6) 0.0067(6) 0.0003(6)
P(3) 2e 0.2709(5) 1/4 0.8918(5) 0.023(1) 0.018(1) 0.020(1) 0 0.0061(9) 0
References
1. Wittmann, M.: Darstellung, Struktur und Eigenschaften von Polyphos- phiden und Polyaiseniden der Seltenerdmetalle. Dissertation, Universität Münster, Germany 1977.
2. Hartweg, M.: Über physikalische Eigenschaften der Seltenerd-Pentaphos- phide LnPs, von СеРг und LaAs2, sowie zur Kenntnis einiger neuer temärer Alkalimetall-Europium-Pnictide. Dissertation, Universität Stutt- gart, Germany 1987.
3, Wichelhaus, W.; von Schnering, H. G.: Die Pentaphosphide des Lanthans und Neodyms, LaPs und NdPs. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 419 (1976) 77-86.
4. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXTL, an integrated system for solving, refining and displaying crystal structures from diffraction data. University of Göttingen, Germany 1978.