Hochschule Worms Faculty Economic Science Course of Studies International Management M. A.
Handbook of Modules
International Management M.A.
Hochschule Worms I Erenburgerstr. 19 I 67549 Worms
Course of Studies International Management (Master of Arts) Hochschule Worms
Content
1. Overview, Structure and Qualification ... 1
1.1 Overview over the Course of Studies International Management M.A. ... 1
1.2 Structure of the studies and scientific qualification ... 2
1.3 Pursuing a skilled employment ... 4
1.4 Developing Personality and Commitments to civil society ... 5
2. Description of Modules and Units ... 6
2.1 Overview: 1st Semester ... 7
Module: Strategic Planning ... 8
Module: Leadership ... 14
Module: Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development ... 17
Module: Overall Economic Framework Conditions ... 27
2.2 Overview: 2nd Semester ... 30
2.2.1 Focus Module: Marketing ... 31
Module: International Marketing ... 33
Module: Retail Marketing ... 39
Module: Distribution Management ... 45
2.2.2 Focus Module: Finance and Controlling ... 54
Module: Financial Accounting ... 56
Module: Financial Management ... 60
Module: International Controlling ... 64
2.2.3 Focus Module: General Management of Retail Companies ... 67
Module: General Management ... 70
Module: Strategic Global Sourcing ... 79
Module: Retail Marketing ... 84
2.3 Overview: 2nd Semester ... 91
Additional Module: Applied Business Informatics... 92
Additional Module: Business Relations ... 97
Additional Module: Tourism-Management ... 103
Additional Module: Energy Trading ... 114
Additional Module: Taxation ... 120
2.4 Overview: 3rd Semester ... 124
Module: Practical Semester/Project ... 125
Module: Studying Abroad ... 126
2.5 Overview: 4th Semester ... 128
Module: Transfer Module ... 129
Module: Master-Thesis ... 135
Course of Studies International Management (Master of Arts) Hochschule Worms
1. Overview, Structure and Qualification
1.1 Overview over the Course of Studies International Management M.A.
The course of studies International Management M.A., based upon an academic degree in the field of business management, enlarges and deepens the knowledge of business management (professional expertise) as well as the generic competencies (methodological and social skills) in order to prepare the students for a practical-professional or a scientific activity in senior management. The course of studies has a modular structure which leads to a standard period of study of four semesters. The graduates are conferred the academic title ‘Master of Arts’. The academic training includes
general as well as specialist and job-oriented knowledge by being scientifically grounded and application-oriented at the same time.The following qualification aims are consequently implemented through the variety and structure of the modules as well as through the modules’ scientific application and practice:
Scientific Qualification
The students are qualified to understand business managerial knowledge and methodically use this knowledge in practice by absorbing knowledge in a scientific oriented way (scientific application orientation).
Qualification for pursuing a skilled employment
The studies qualify to take up an employment in a business-oriented professional and management position in globally oriented and internationally operating companies by imparting knowledge, comprehension and expertise/skills.
Developing Personality and extending it to commitments to civil society
The studies impart coherences of knowledge, comprehension and expertise/skill by integrating
methodological and social competencies (generic competencies) in order to enable a
development of personality and thereby establishing the basis for commitments to civil society.
Course of Studies International Management (Master of Arts) Hochschule Worms
1.2 Structure of the studies and scientific qualification
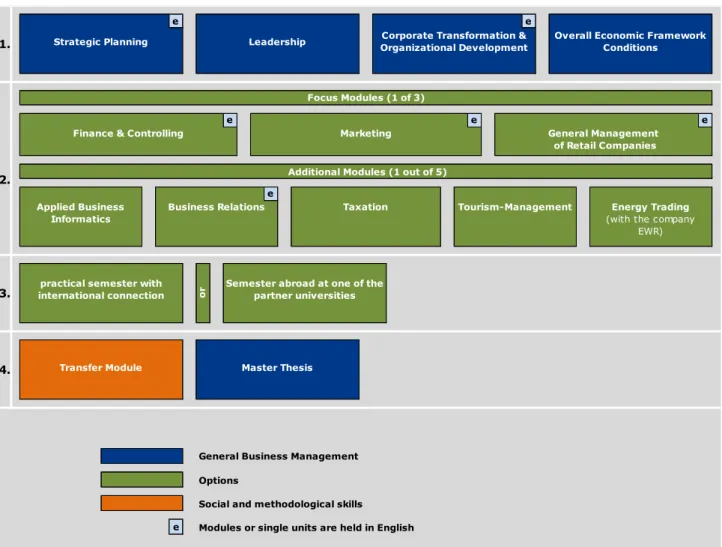
Internationality builds the framework of this consecutive Master- Course of Studies. Above all it can be found in the curricular substance of studies, but also in the basic structure of the curriculum through the obligatory integration of a semester abroad respectively a practical semester abroad
1.
The language skills of the students are consequently developed through courses held in English such as “Corporate Transformation/Organizational Development”. Furthermore international guest lecturers are structurally integrated in the curriculum.
In doing so a useful mixture of German and English courses was targeted, so that the students find a balanced overall concept. Moreover the admission requirements for this master studies include a degree qualifying for profession as well as knowledge in foreign languages. The students need to have at least level C1 in English as well as level A2 in another foreign language
2.
120 Credit Points are needed for graduating in International Management M.A. . These points are consistently distributed over four semesters.
The first semester includes the following four basic modules that are based on the first level of university education and which deepen and expand the knowledge of the basic management functions: “Strategic Planning”, “Leadership”, “Corporate Transformation/Organizational Development” and “Overall Economic Framework Conditions”. The strategic aspects and implications are specifically emphasized. These three modules are completed through the legal and economic perspective, which is lectured in the module “Overall Economic Framework Conditions”.
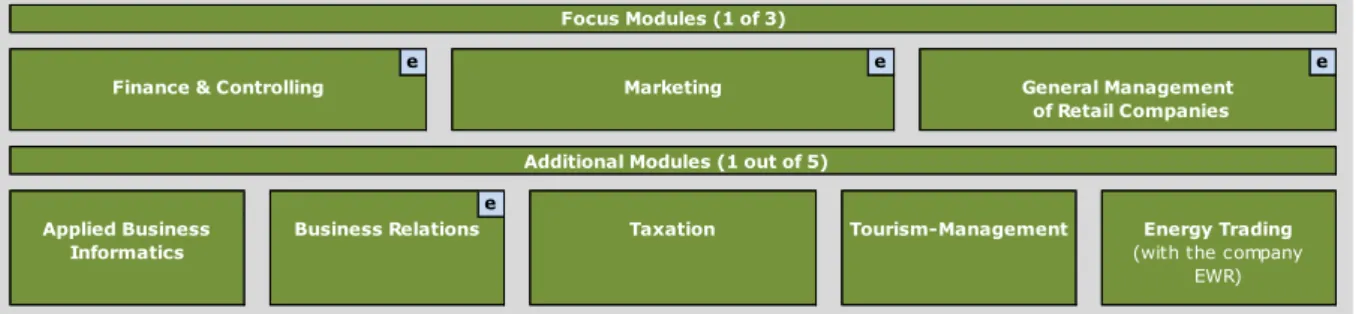
In the second semester the students choose one focus module and one additional module, based on their personal and job-related intended ambition.
This provides an optimal possibility for the students for personally profiling.
The students can basically choose between the following options
3:
1 There might be exceptions that allow doing a practical semester in Germany, which is done in an international context.
2 http://www.hs-worms.de/Zulassungsvorraussetzungen.1487.0.html
3 The offered courses are variable. The offer depends on a minimum number of participants. There is no guaranty that each additional module is offered each semester.
Course of Studies International Management (Master of Arts) Hochschule Worms
Figure 1: Overview over the focus and additional modules
During the
third semester the students absolve an integrated phase of studies at a partneruniversity abroad. The global net of currently 120 partner universities
4basically guarantees a stay in the desired language area of the students. The recognition of the course credits, which are done abroad, is based upon a Learning Agreement with the course of studies. It is concluded with the course of studies before studying abroad based on the current course offer of the partner university in order to secure the recognition of course credits. This document is signed by the student, the course of studies as well as by the partner university. After completing the studies abroad the stipulated course credits of the Learning Agreement are recognized at sight of the transcript of records of the foreign partner university. Furthermore the students have the possibility to replace the studies abroad through an internship in a company abroad which helps them to make (first) practical experiences on the international employment market.
The
fourth and last semester consists of one transfer module and the master thesis. The transfermodule is composed of a corporate strategic planning simulation and an applied Assessment- Center-Training, which focuses a preparation for future situations of applications for employment.
Furthermore the strategic planning simulation requires the concentrated application of the business managerial knowledge and competencies acquired during the studies. The master thesis includes a written paper and a colloquium.
In total the students are qualified by the master course of studies of International Management to undertake a scientific or practical employment through its application-oriented form.
4 Currently there are round about 40 partner universities accessible for the master-program.
e e e
e
Focus Modules (1 of 3)
Additional Modules (1 out of 5)
Applied Business Informatics
Business Relations
General Management of Retail Companies
Finance & Controlling Marketing
Taxation Tourism-Management Energy Trading (with the company
EWR)
Course of Studies International Management (Master of Arts) Hochschule Worms
e e
e e e
e
General Business Management Options
Social and methodological skills
e Modules or single units are held in English
4. Transfer Module Master Thesis
3. practical semester with international connection
Semester abroad at one of the partner universities
or
Focus Modules (1 of 3)
2. Additional Modules (1 out of 5)
Applied Business Informatics
Business Relations
General Management of Retail Companies
Finance & Controlling Marketing
Taxation Tourism-Management Energy Trading (with the company
EWR) Studienplan - Übersicht
praxisintegrierter Master-Studiengang International Management M.A.
1. Strategic Planning Leadership Corporate Transformation &
Organizational Development
Overall Economic Framework Conditions
Figure 2: Overview over the degree course scheme
1.3 Pursuing a skilled employment
Graduating this master course of studies qualifies the student to successfully pursuit management tasks through their gained professional expertise and generic competencies (methodological and social skills).
Furthermore the students could be engaged in research. Graduates obtain the necessary
qualifications to independently evaluate and respectively classify complex professional decision
situations in globally operating companies in order to make independent decisions based on these
considerations. The educational profile allows the graduates to develop creative and flexible
solution as well as to rapidly understand new, unknown situations and problems. Graduates are
also working confidently in a broad respectively multidisciplinary business managerial context.
Course of Studies International Management (Master of Arts) Hochschule Worms
The synchronized overall concept prepares the students purposefully for working in an international environment and fulfills the practical demands
(Employability). Thereby the course ofstudies International Management M.A. serves the global market, which is characterized by increasing linkage and aggregation. It also counters the steadily growing shortage of professional and managerial staff by preparing and qualifying its graduates for tasks in senior management of nationally and internationally operating companies.
1.4 Developing Personality and Commitments to civil society
The methodological and social skills are consequently trained by the comparatively small semester groups and their very heterogenic character as well as the seminar-like structure of the courses including loads of team- and project work. Training and developing the key competencies, such as communication and conflict skills or working independently, is constantly demanded. Not least the studies contribute to the personal character development of the students, especially through the integrated semester abroad respectively the practical phase in companies.
The consecutive master program aims to impart methodological and social skills, which are relevant for management tasks in senior management positions, as well as to deepen and extend business managerial expertise with consequent international connections.
Furthermore the commitment to civil society of students at the university (such as student social commitments within the AStA, the StuPa, the student union as well as the collaboration on university events such as the annual “International day”) is honored by a university-wide
“Bonusheft” (book of bonus) for social commitment.
Course of Studies International Management (Master of Arts) Hochschule Worms
2. Description of Modules and Units
M. A. International Management 2.1 Overview: 1st Semester
Semester
First semester
Modules Strategic Planning
Leadership
Corporate Transformation/Organizational Development
Overall Economic Framework Conditions Number of the totally assigned
ECTS-credits 30 ECTS
Forms of teaching and studying of the semester
Seminar-like class
Working on Case studies
Working in Groups
Working individually/ Self-Study
Overall view/Description The first semester deepens the basics of the previous Bachelor’s or Diploma’s degree and especially imparts the key competencies for a leading position in management.
M. A. International Management
Module: Strategic Planning
Module-Nr./ Code 1.1
Module Designation Strategic Planning
Semester or Trimester 1. semester
Duration of the Module 1 semester
Course type
(compulsory, optional, etc.)
Compulsory subject
As appropriate courses of this module 1.1.1 Strategic Planning Process 1.1.2 Strategy Implementation Frequency of the module offer Every semester
Entrance requirement None
Applicability of the Module for other courses of study
Suitable for all international business studies programs Responsible person for this module Prof. Dr. Germann Jossé
Name of the Professor Guest lecturer Language of instruction English Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 6 ECTS Total workload and its composition
(e.g. independent study + contact time, etc.)
Total workload: 180 h
Semester hours per week 4 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements for
assigning credits5
Klausur (180 min) oder6 Hausarbeit [examn of 180 min or term paper]
Weighting of the mark within the cumulative grade
According to ordinances and regulations
Qualification aims of the module The goal of this module is the transfer of knowledge for modern planning instruments in strategic and operative planning.
Professional competence:
To know and understand the goals, tasks and processes of management within the scope of planning; transfer of different strategic and operative tools
Methodological competence:
Application and adaption of the learned contents in the scope of different international practical cases and case studies
Key competence:
Ability to develop and to formulate strategies for a concrete, previously announced practical case with international context as well as to implement these strategies against the background of an international environment; ability to perform strategic and operative planning for companies independently as well as to present the solutions professionally in front of an expert audience.
5 The language in which the examination has to be completed is generally conform to the language spoken in the module.
6 The professor announces the type of examination at the beginning of the semester.
Contents of the modules See Unit Descriptions below Forms of teaching and studying of the
module
Dialogue-oriented inputs of lecturer
Analysis of multi-national planning approaches of companies
Group works, team-based projects regarding strategic analysis and derivation of strategies
Elaboration of international case studies, in some cases with cooperation partners
Foreign guest lecturers Special characteristics (e.g. online-
amount, field trips, guest lecturers, etc.)
Foreign guest lecturers
literature
(compulsory reading/ additional recommended literature)
See Unit Descriptions below
M. A. International Management
Unit Description of the Module: Strategic Planning
Code 1.1.1
Module Designation Strategic Planning
Designation of the course/unit Strategic Planning Process
Professor Guest Lecturer
Language of instruction of the unit
English Number of the assigned ECTS-
credits
3 ECTS Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Lecture: 30 h
Self-study/ preparation & follow-up of lecture: 20 h
Elaboration of topic: 20 h
Case Study: 20 h
Total: 90 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit
2 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/
Requirements for assigning credits
See Module Description
Weighting of the mark within the cumulative grade
According to ordinances and regulations Contents of the unit I. Framework:
The St. Gallen management model
Goals and Tasks of strategic management
Creating of vision and mission statement
The 6-stage-concept for construction of strategic management II. Tool-Set of strategic planning:
The PIMS-program
SWOT-Analysis
Strategic balance
Experience curve effects
Competition within an industry
From BCG-Matrix to integrated portfolio management III. Implementation of strategic planning:
Planning model
Strategic analysis
Derivation of strategies
Strategies of internationalization
Analysis based on practical cases
Forms of teaching and studying of the unit
Input by the lecturer Coached literature review
Case studies regarding decision problems Group discussions
Presentations of theses Special characteristics (e.g.
online-amount, field trips, guest lecturers, etc.)
Guest lecture by foreign guest lecturers
Compulsory reading Barney/Hesterly: Strategic Management and Competitive Advantage:
Concepts and Cases
Katsioloudes: Strategic Management: Global Cultural Perspectives for Profit and Non-Profit Organizations
Katsioloudes: Global Strategic Planning Grant: Strategic Management
Grant: Contemporary Strategic Analysis
Hunger/Wheelen: Essentials of Strategic Management Additional recommended
literature
Kreilkamp: Strategisches Marketing und Management Müller/Stewens: Strategisches Management
Lombriser/Abplanalp: Strategisches Management Kerth et al.: Die besten Strategietools in der Praxis Huber: Praxishandbuch Strategische Planung
M. A. International Management
Unit Description of the Module: Strategic Planning
Code 1.1.2
Module Designation Strategic Planning
Designation of the course/unit Strategy Implementation
Professor Guest Lecturer
Language of instruction of the unit English Number of the assigned ECTS-
credits
3 ECTS
Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Lecture: 30 h
Self-study/preparation & follow-up of lecture: 20 h
Topic elaboration: 20 h
Case study: 20 h
Total: 90 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit
2 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements
for assigning credits
See Module Description Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to ordinances and regulations
Contents of the unit Operative planning based on the St. Gallen management model
Integrated operative planning
Concept of bottleneck planning and removal of bottlenecks
Sales planning
F&E planning
Procurement planning
Production planning
HR planning
Planning of support functions
Integration and coordination of planning processes Forms of teaching and studying of
the unit
Input of lecturer
Case studies regarding decision problems
Group projects regarding practice-oriented planning problems Special characteristics Guest lecture by foreign guest lecturers
Compulsory reading Russell, R.: Operations Management: Creating Value Along the Supply Chain, Wiley & Sons (latest edition)
Slack, N.; Chambers, S. & Johnston, R.: Operations and Process Management: Principles and Practice for Strategic Impact, Prentice Hall (latest edition)
Slack, N.; Chambers, S. & Johnston, R.: Operation Management, Prentice Hall (latest edition)
Verweire, K.; Van de Berghe, L. (ed.): Integrated Performance Management: A Guide to Strategy Implementation, Sage (latest ed.)
Additional recommended literature
Abele, E.; Meyer, T. et al.: Global Production: A Handbook for Strategy and Implementation, Springer (latest edition)
Goffin, K. and Mitchell, R.: Innovation Management: Strategy and Implementation Using the Pentathlon Framework
Palgrave Macmillan (latest edition)
Hahn/Hungenberg: Planung & Kontrolle
Reichmann: Controlling mit Managementberichten
Horváth: Controlling
Graumann: Fallstudien zum Controlling
Troßmann/Baumeister/Werkmeister: Management-Fallstudien im Controlling
David: Strategisches Management von Controllerbereichen
M. A. International Management
Module: Leadership
Module-Nr./ Code 1.2
Module Designation Leadership
Semester or Trimester 1. Semester Duration of the Module 1 Semester Course type
(Compulsory, optional, etc.)
Compulsory subject As appropriate courses of this
module
1.2.1 Leadership Management Frequency of the module offer Every semester
Entrance requirement none
Applicability of the Module for other courses of study
Suitable for all international business studies programs Responsible person for this
module
Prof. Dr. Peter Mühlemeyer Name of the Professor Prof. Dr. Peter Mühlemeyer Language of instruction German
Number of the assigned ECTS- credits
9 ECTS Total workload and its
composition (e.g. independent study + contact time, etc.)
Total Workload: 270 h
Semester hours per week 6 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements
for assigning credits7
Hausarbeit und mündliche Prüfung (15 min) (term paper and oral examination of 15 min]
Weighting of the mark within the cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Qualification aims of the module Within the first year of these studies this basic module ensures the leadership skills of the students in the field of operational management processes.
Professional Expertise:
After giving a historical overview over the topic area “Leadership” and after discussing the epochal leadership styles, evolutionary-psychological aspects are covered as well as professional expertise, which is demanded for leaders nowadays, is taught.
Methodological competence:
The students gain an overview over the topic area “Leadership” by doing own and coached research. Furthermore they learn how to evaluate methods of leadership and how to apply those in a corporate context.
Core competencies
The course aims especially to counter the operational reality, which is characterized by a constantly growing complexity and dynamic, by using appropriate management instruments.
7 The language in which the examination has to be completed is generally conform to the language spoken in the module.
Contents of the modules See Unit Descrription Forms of teaching and studying of
the module
Input by the professor, topic presentations by the participants Special characteristics (e.g. online-
amount, field trips, guest lecturers, etc.)
Among others Acquiring the topics with subsequent group discussions
literature
(compulsory reading/ additional recommended literature)
Compulsory Reading:
Weibler, J.: Personalführung, München (aktuellste Auflage) von Rosenstiel et al: Führung von Mitarbeitern/Fallstudien zum Personalmanagement, Stuttgart (aktuellste Auflage)
Staehle, W.: Management, München (aktuellste Auflage) Additional literature (professional journals):
PERSONAL Personalführung zfo
Harvard Business Manager
M. A. International Management
Unit Description of the Module: Leadership
Code 1.2.1
Module Designation Leadership
Designation of the course/unit Leadership Management
Professor Prof. Dr. Peter Mühlemeyer
Language of instruction of the unit German Number of the assigned ECTS-
credits
9 ECTS
Workload of this unit Total Workload 270h
Composition of the Workload Lecture: 90 h
Self-study/ preparation & follow-up of lecture: 120 h
Exam incl. Preparation: 60 h
Total: 270 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit
6 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements
for assigning credits
According to the Module Description Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances Contents of the unit I. Stage of Orientation
1. What is leadership?
2. Communication as elementary leadership task
3. Leadership paradigms: Social fact vs. Social Construction 4. Leading and being leaded in groups
5. Synthesis of modern Leadership Science II. Independent Study(coached)
1. Analysis of literature to the topic area „Leadership, Management Approaches, Change Management”
2. Project work: Preparation/Processing practical cases III. Practical Week
1. Reflection of the results of the independent study
2. Discussion of the results and reflection of the case studies 3. Excursion/ Presentation of current company-cases
Forms of teaching and studying of the unit
Input by the professor, topic presentations by the participants Special characteristics (e.g. online-
amount, field trips, guest lecturers, etc.)
Among others Acquiring the topics with subsequent group discussions
Compulsory reading Compulsory Reading:
Weibler, J.: Personalführung, München (aktuellste Auflage) von Rosenstiel et al: Führung von Mitarbeitern/Fallstudien zum Personalmanagement, Stuttgart (aktuellste Auflage)
Staehle, W.: Management, München (aktuellste Auflage) Additional recommended literature Additional Literatur (professional journals):
PERSONAL, Personalführung, zfo, Harvard Business Manager Kastner, M.: SynEgoismus
Malik, F.: Führen, leisten, leben
M. A. International Management
Module: Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development
Module-Nr./ Code 1.3
Module Designation Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development
Semester or Trimester 1. semester
Duration of the Module 1 semester
Course type(compulsory, etc.) Compulsory subject As appropriate courses of this module 1.3.1 Crafting Strategy
1.3.2 Organizational Learning
1.3.3 Dynamic Strategy & Strategic Renewal Frequency of the module offer Every semester
Entrance requirement Knowledge in English language
Solid understanding of (traditional) organizational theories (e.g.
new institutional economics, institutionalism) Applicability of the Module for other
courses of study
All business related course of studies Responsible person for this module Prof. Dr. Jörg Funder
Name of the Professor Prof. Dr. Jörg Funder/
International visiting professors:
Guilherme Albieri (State University of New York, USA)
Prof. John Gamble (Mitchell School of Business, USA) or other
Language of instruction English
Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 9 ECTS Total workload and its composition 270 h
Semester hours per week 6 SWS
Examination type/ Requirements for assigning credits8
Klausur (120 min) und Hausarbeit [examination of 120 min and term paper)
Weighting of the mark within the cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Qualification aims of the module Students will develop a solid understanding of advanced organizational & corporate transformation theories. Tools and methodolgies to successfully transform organizations are taught.
Participants will also build professional competences on faciliting and managing corporate change programms.
Professional Competence:
(A) Crafting Strategy
Understand dynamics of ‘new’ strategy
Understand how companies need to be structured for continuous self-renewal & dynamic strategies
(B) Organizational Learning
Understand importance of knowledge creation and knowledge management for competitive advantage
Convey basic principles of creating a knowledge-driven company to students
8 The language in which the examination has to be completed is generally conform to the language spoken in the module.
Understand difficulties to balance different learning modes within an organization
Understand leadership challenges in learning organization (C) Dynamic Strategy & Strategic Renewal
Learn about basic concepts of strategic renewal
Understand the correlation of ‚organizational alignment’ and competitive advantage
Understand the interdependence of structure, process, systems and culture to implement strategic renewal processes
Understand the impact and interaction of resources and capabilities in the context of dynamic environmental changes Methodological Competence:
(A) Crafting Strategy
Identify and evaluate complexities in dynamically changing and fast pace environments
(C) Dynamic Strategy & Strategic Renewal
Identify and evaluate the readiness and necessity for strategic renewal
Key Competence:
(A) Crafting Strategy
Being able to distinguish ‚initiative formulation’ vs. ‚initiative formation’
Understand requirements / prerequisites for a successful strategic leadership
B) Organizational Learning
Discuss impact of organizational blind spots and core beliefs on organizational change & learning
(C) Dynamic Strategy & Strategic Renewal
Being able to indicate success factors of a high-level transformation journey
Contents of the modules See unit descriptions Forms of teaching and studying of the
module
Lecture/ Coached self-study/ Team project with short presentation/ Case studies
Special characteristics Guest lectures on selected topics
literature See unit descriptions
M.A. International Management
Unit Description of the Unit: Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development
Code 1.3.1
Module Designation Corporate Transformation / Organisational Development Designation of the course/unit Crafting Strategy (Unit 1)
Professor Prof. Dr. Jörg Funder/Guest professor
Language of instruction of the unit English Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 3 ECTS
Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Contact Self-study
Lecture: 25 h 30 h
Self-study/project:
Exam prep: 5 h 30 h
Sum: 30 h 60 h
Total: 90 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit 2 SWS Examination type/ Requirements for
assigning credits
See module description Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances Contents of the unit 1. Basics of strategic transformation
Strategic transformation & competitive advantage
Strategic imperatives: positioning & differentiation
Stakeholder vs. shareholder approaches
Management of transformation ‘power flower’
2. Evaluation of business contexts and company resources
Industrial & institutional context
Core competences of the firm
Integration of context & company analysis 3. Types of transformation initiatives
Market based initiatives
Competitive based initiatives
Corporate based initiatives
Value generation strategies
(Disruptive) innovation based initiatives 4. Evaluation of transformation initiatives
Selection criteria
Selection methods Forms of teaching and studying of the
unit
Lecture & Case Studies Special characteristics (e.g. online-
amount, etc.)
- International Visiting Professor(s) - Guest lectures on selected topics
Compulsory Reading - Course reader with selected strategy articles from leading strategy & organizational journals
- Müller-Stewens/ Lechner : Der General Management Navigator: Wie strategische Initiativen zum Wandel führen“, Schaeffer-Poeschl. latest edition
- Course reader
- Case studies provided in course
Additional recommended literature - Thompson, A., Strickland, J., Gambe, J., Jain, A.: „Crafting and Executing strategy – the quest for competitive advantage“, McGraw Hill – latest edition
- Eisenhardt, M.K., Sull, N.D. (2001): „Strategy as simple rules“, Harvard Business Review, January, 107-116.
- Eisenhardt, M.K. (2002): „Has strategy changed? “, Sloan Management Review, Winter, 8-91.
- Core Management Journals such as Strategic Management Journal, Academy of Management Journal, Journal of Retailing, Journal of International Retail & Distribution Management, McKinsey Quarterly (online).
M.A. International Management
Unit Description of the Unit: Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development
Code 1.3.2
Module Designation Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development Designation of the course/unit Organizational Learning (Unit 2)
Professor Prof. Dr. Jörg Funder
Language of instruction of the unit English Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 3 ECTS
Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Contact Self-study
Lecture: 30 h 35 h
Self-study/ project: 25 h
Exam prep:
Sum: 30 h 60 h
Total: 90 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit 2 SWS Examination type/ Requirements for
assigning credits
See module description Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances Contents of the unit 1. Knowledge-based theory of the firm
2. Organizational (un)learning 3. Organizational ambidexterity Forms of teaching and studying of the
unit
Self-study/Lecture/Coached team project/
Feedback on final presentation of team project Special characteristics (e.g. online-
amount, field trips, guest lecturers, etc.)
- Developing concept based on self-selected team project - On-going online coaching (virtual classroom)
Compulsory Reading Knowledge-based theory of the firm
- Grant (1996): „Towards a knowledge based theory of the firm“, Strategic Management Journal, Winter 1996, 17, 109-122.
- Nonaka/ vonKrogh (2009): „Tacit knowledge and knowledge conversion: controversy and advancement in organizational knowledge creation theory“, Organization Science, May/ June 2009, 635-652.
Organizational (un)learning
- Senge, Peter M.: „Die fünfte Disziplin; Kunst und Praxis der lernenden Organisation“, Schäffer-Poeschel, Stuttgart. Latest edition
- Akgün et al. (2007): „Organizational unlearning as change in beliefs and routines in organizations“, Journal of Organizational Change Management, 20, 6, 794-812.
- Starbuck/ Nystrom (1984): „To avoid an organizational crisis, unlearn“, Organizational Dynamics, 12, 4, 53-65.
Organizational Ambidexterity
- Tushman et al. (2010): „Exploration and exploitation within and across organizations“, The Academy of Management Annals, 4, 1, 109-155.
- Tushman/ O’Reilly (1996): „Ambidextrous organizations:
managing evolutionary & revolutionary change“, California Management Review, 38, 4, 8-30.
- Birkinshaw/ Gibson (2004): „Building ambidexterity into an organization“, MIT Sloan Management Review, Summer 2004, 47- 55.
Additional recommended literature Knowledge-based theory of the firm
- Nonaka (1994): „A dynamic theory of knowledge creation“, Organization Science, 5:1, 14-27.
- Nonaka (1998): „The science of ‚Ba’: building the foundation for knwoledge creation“, California Management Review, 40, 3, 40- 54.
Organizational (un)learning
- March (1991): „Exploration and Exploitation in organizational learning“, Organization Science, 2,1,71-89.
- Klein (1989): „Parenthic learning in organizations: toward the unlearning of the unlearning model“, Journal of Management Studies, 26, 3, 291-308.
- Lembke, Gerald (2004): “Die lernende Organisation; als
Grundlage einer entwicklungsfähigen Unternehmung”, Tectum, Marburg.
Organizational Ambidexterity
- Gibson/ Birkinshaw (2004): „The antecedents, consequences, and mediating role of organizational ambidexterity“, Academy of Management Journal, 47, 2, pp. 209-226
M.A. International Management
Unit Description of the Unit: Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development
Code 1.3.3
Module Designation Corporate Transformation / Organizational Development Designation of the course/unit Dynamic Strategy & Strategic Renewal (Unit 3)
Professor Prof. Dr. Jörg Funder
Language of instruction of the unit
English Number of the assigned ECTS-
credits
3 ECTS Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Exam Team project
Contact Self-Study Contact Self-Study
Lecture: 24 h 45 h 24 h 45 h
Self-study/ project: 6 h 15 h
Exam prep: 6 h 15 h
Sum: 30 h 60 h 30 h 60 h
Total (either exam or team project):
90 h Semester hours per week of the
Unit
2 SWS Examination type/ Requirements
for assigning credits
See module description Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Contents of the unit 1.
Organizations as complex adaptive systems
2. Dynamic strategy & strategic renewal3. Organizational routines
4. Path dependency & path creation 5. Transforming the resource-base
6. Transforming the capability base (dynamic resource-based strategies)
7. Business model transformation 8. Additional topics
Forms of teaching and studying of the unit
- Lecture
- Student presentations on selected topics - Case studies where applicable
Special characteristics (e.g.
online-amount, lecturers, etc.)
Guest lectures on selected topics
Compulsory Reading Organizations as complex adaptive systems
- Anderson (1999) : “Complexity Theory and Organization Science, Organization Science, 10, 3, 216-232.
- Pascale (1999): “Surfing the Edge of Chaos”, Sloan Management Review, 83-94.
Dynamic strategy & strategic renewal
- Porter (1996): „What is strategy? “, Harvard Business Review, November – December, 61-78.
- Lovas/ Ghosal (2000): „Strategy as guided evolution“, Strategic Management Journal, 21, 875-896.
- Nelson (1991): “Why Do Firms Differ, and How Does it Matter?“, Strategic Mangement Journal, 12, 61-74.
- Kogut & Zander (1996) : “What Firms Do? Coordination, Identity, and Learning“, Organizational Science 7, 5, 502-518.
- Amit & Shoemaker (1993) : “Strategic Assets and Organizational Rents“, Strategic Management Journal, 14, 1, 33-46.
- Reeves & Deimler (2011) : “Adaptability: The New Competitive Advantage”, HarvardBusinessReview, 135-141.
Organizational Routines
- Parmigiani & Howard-Grenville (2011) : “Routines Revisited:
Exploring the Capabilities and Practice Perspectives”, The Academy of Management Annals, 5,1, 413–453
- Pentland/ Harerem/ Hillison (2010) : “Comparing Organizational Routines as Recurrent Patterns of Action“, Organization Studies, 31, 07, 917-940.
- Pentland/ Feldman/ Becker/ Liu (2012) : “Dynamics of Organizational Routines: A Generative Model“, Journal of Management Studies, 49, 8, 1484-1508
Path creation
- Sydow/ Schreyögg et al. (2009): „Organizational path dependence:
opening the black box“, Academy of Management Review, 34, 4, 689-709.
- Garud/ Karnoe (2010): „Path dependence or path creation?“, Journal of Management Studies, 47, 4, 760-774.
Transforming the resource-base
- Peteraf (1993): „The cornerstones of competitive advantage: a resource-based view“, Strategic Management Journal, 14, 3, 179- 191.
- Gant (1996): „The resource based view of theory of competitive advantage: implications for strategy formulation“, California Management Review, 33, 3, 114-135.
Transforming the capability base (dynamic resource-based strategies) - Helfat/ Perteraf (2003): „The dynamic resource based view:
capability lifecycles“, Strategic Management Journal, 24, 10, 997- 1010.
- Eisenhardt/ Martin (2000): „Dynamic capabilities: what are they?“, Strategic Management Journal, 21, 10, 1105-1121.
- Barreto (2010): „Dynamic Capabilities: A Review of Past Research and an Agenda for the Future“, Journal of Management, 34, 256- 288.
Business Model Transformation
- Doz/ Kosonen (2010): „Embedded strategic agility: a leadership agenda for accelerating business model renewal“, Journal of Long Range Planning, 43, 2.
- Casadesus-Masanell/ Ricart (2007): „Competing though business models“, Working Paper # 713, IESE Business School, Nov. 2007.
Additional topics
- Literature to be provided based on selected topics
Case Series (might be subject to change, please refer to current term course syllabus)
- Collis (2005): Ben & Jerry’s Homemade Ice Cream Inc.: A Period of Transformation, HBS Case # 9-796-109.
- Gavetti/ Tripsas (2007): Polaroid: Entering digital imaging, Harvard Business School Case # 9-706-459.
- Bartlett/ Ginska (2005): GE’s Digital Revolution: Redefining the ‚E’ in GE, HBS Case # 9-302-001.
- Nada/ Bartlett (1994): Intel Corporation - Leveraging Capabilities for Strategic Renewal, HBS Case # 9-394-141.
- Mazutis/ White/ Beamish (2008): Research in Motion: Managing Explosive Growth, Richard Ivey School of Business Case # 908M46.
Fahrfoomand (2006): SAP Platform Strategy, University of Hongkong Case # HKS564.
Additional recommended literature
Organizations as complex adaptive systems
- Stacey (1995): “The Science of Complexity: An Alternative
Perspective for Strategic Change Processes“, Strategic Management Journal, 16, 6, 477-495.
- Stacey (1993) : “Strategy as Order Emerging from Chaos”, Long Range Planning, 26, 1, 10-17.
Dynamic strategy & strategic renewal
- Mintzberg/ Westley (1992): „Cycles of organizational change“, Strategic Management Journal, 13, 39-59.
- Nelson (1991): „Why do Firms Differ, and How Does it Matter?“, Strategic Management Journal, 12, Special Issue: Fundamental Research Issues in Strategy and Economics (Winter 1991), 61-74.
- Ghemawat (1999): „Strategy and the business landscape“, Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Organizational routines
- Feldman & Pentland (2003) : “Reconceptualizing Organizational Routines as a Source of Flexibility and Change“, Administrative Science Quarterly, 48, 94–118.
- Becker (2004) : “Organizational routines. a review of the literature”, Industrial and Corporate Change, 13, 4, 643-677
Path dependence & creation
- David (2000): „Path dependence, it’s critiques and the quest for
‚historical economics’“, Working Paper, Oxford University, June 2000
- Garud/ Karnoe (2000): „Path Creation as a Process of Mindful Deviation“, in Koski/ Marttila (eds) Proceedings: Conference on Knowledge and Innovation, pp. 234–267. Helsinki: Helsinki School of Economics and Business Administration, Centre for Knowledge and Innovation Research.
- Koch (2011) : “Inscribed Strategies: Exploring the Organizational Nature of Strategic Lock-in“, Organization Studies, 32, 3, 337–363.
- Sydow & Schreyögg (2012) : “ORGANIZATIONAL PATH DEPENDENCE:
OPENING THE BLACK BOX“, Academy of Management Review, 34, 4, 689–709.
Transforming the resource-base
- Wernerfeld (1984): „A resource-based view of the firm“, Strategic Management Journal, 5, 2, 171-180.
- Barney, J. B. (1995): „Looking inside for competitive advantage“, Academy of Management Executive, 9(4), 49-65.
- Priem/ Butler (2001): „Is the resource-based „view“ a useful perspective for strategic management research?“, Academy of Management Review, 26,1 1, 22-40.
- Kraijenbrink/ Spender/ Groen (2010): „The resource-based view: a review and assessment of its critiques“, Journal of Management, 36,1, 349-372.
Transforming the capability base (dynamic resource-based strategies) - Teece et al. (1997): „Dynamic capabilities and strategic
Management“, Strategic Management Journal, 18, 7, 509-533.
- O‘Reilly/ Tushman (1997): „Ambidexterity as a dynamic capability:
resolving the innovator‘s dilemma“, Working paper, HBS Working Paper # 07-088, May 2007.
- Zollo/ Winter (2002): „Deliberate learning and the evolution of dynamic capabilities“, Organization Science, 13, 3, 339-351.
- Rindova/ Kotha (2001): „Continuous morphing: competing through dynamic capabilities, form, and function“, Academy of Management Journal, 44, 6, 1263-1280.
Business Model Transformation
- Amit/ Schoemaker (1994): „Strategic assets and organizational rent“, Strategic Management Journal, 14, 33-46.
- Zott/ Amir (2010): „Business model design: an activity system perspective“, Journal of Long Range Planning, 43, 2.
- Baden-Fuller/ MacMillan/ Demil/ Lecoc (2010): Special issue on business models, Journal of Long Range Planning, 43, 2.
- Teece (2010) : “Business Models, Business Strategy and Innovation“, Long Range Planning 43, 172-194.
- Smith, Binns & Tushman (2010) : “Complex Business Models:
Managing Strategic Paradoxes Simultaneously“, Long Range Planning, 1-14.
Additional topics
- Literature to be provided based on selected topics
M. A. International Management
Module: Overall Economic Framework Conditions
Module-Nr./ Code 1.4
Module Designation
Overall Economic Framework Conditions
Semester or Trimester 1st SemesterDuration of the Module 1 Semester
Course type(compulsory, etc.) Compulsory subject
As appropriate courses of this module 1.4.1 International economic policies 1.4.2 Public International Law Frequency of the module offer Every semester
Entrance requirement none
Applicability of the Module for other courses of study
Suitable for all international business studies programs Responsible person for this module Prof. Dr. Schilling
Name of the Professor Prof. Dr. Schilling/
Contract Teacher Christian Koch
Language of instruction German
Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 6 ECTS
Total workload and its composition Total Workload: 180 h Semester hours per week 4 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements for
assigning credits9
Klausur (180 min) [examination of 180 min]
Weighting of the mark within the cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Qualification aims of the module According to the identically named Bachelor-Module this Module is meant to impart the neighbor disciplines of the management, which are international economic policies and basics of the public international law. These subjects intend to classify the impacts of these disciplines regarding entrepreneurial decisions.
Professional Expertise:
Advanced impartation of essential contents in the area of international economic policies which frames to some extent the contents of public international law.
Methodological Competence
The knowledge is applied by working on case studies and Models that have an international connection
Key competencies
Identifying and evaluating the disciplines‘ impacts on the economy – beyond their classical knowledge area
Contents of the modules See Unit Descriptions Forms of teaching and studying of the
module
Input by the professor
Special characteristics Among others: the documents can be found on the moodle platform
literature See Unit Descriptions
9 The language in which the examination has to be completed is generally conform to the language spoken in the module.
M. A. International Management
Unit Description of the Module: Overall Economic Framework Conditions
Code 1.4.1
Module Designation
Overall Economic Framework Conditions
Designation of the course/unit International Economic PoliciesProfessor Prof. Dr. Dirk Schilling
Language of instruction of the unit German Number of the assigned ECTS-
credits
3 ECTS
Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Lecture: 30 h
Self-study/ preparation & follow-up of lecture: 38,5 h
Working on topics: 20 h
Examination time: 1,5 h
Total: 90 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit
2 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements
for assigning credits
See Module Description Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Contents of the unit 1.
Basics of the international economic policies
1.1. Elements of the globalization1.2. Institutions of the international economic policies 2.
Microeconomical Funding of international economic
policies
2.1. Price Policy2.2. Regulation and Deregulation 2.3. Competition Policy
3.
Macroeconomical Funding of international economic policies
3.1. Fighting inflation by monetary policy 3.2. Cyclical Stabilization
3.3. Payments Balance and Exchange Rate Policies
4.
Aims of the international economic policies: Applying Welfare Economics
4.1. Economic Analysis of collective evaluations 4.2. Aims and target conflicts of economic policies 5. Operationalization of particular
Forms of teaching and studying of the unit
Input of the professor, Case Studies regarding decision problems Special characteristics Working on Case Studies
Compulsory reading Klump: Wirtschaftspolitik, aktuellste Auflage Additional recommended
literature
Fritsch et al., Marktversagen und Wirtschaftspolitik Mussel/Pätzold, Grundfragen der Wirtschaftspolitik
M. A. International Management
Unit Description of the Module: Overall Economic Framework Conditions
Code 1.4.2
Module Designation Overall Economic Framework Conditions Designation of the course/unit Public International Law
Professor Contract Teacher Christian Koch
Language of instruction of the unit
German Number of the assigned ECTS-
credits
3 ECTS Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Lecture 30 h
Self-study/ preparation & follow-up of lecture: 58,5h h
Examination Time: 1,5 h
Total: 90 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit
2 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/
Requirements for assigning credits
See Module Description
Weighting of the mark within the cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances Contents of the unit 1. Basics
1.1 Sources of Law
1.2 Law of Nations, European Law, National Law 1.3 Public Law vs. Private Law
2. Constitutional Law 2.1 General Basics
2.2 Specific fundamental rights (constitutional freedom of profession, right of property)
2.3 Protection of the Constitutional Law 3. EC-Law
3.1 Basics, Institutions
3.2 European Law and Economic Policies 4. Administrative Law
Forms of teaching and studying of the unit
Input of the Professor, Case Studies regarding decision problems Special characteristics (e.g.
online-amount, field trips, guest lecturers, etc.)
None
Compulsory reading Wolffgang, H.-M.: Öffentliches Recht und Europarecht, aktuelle Auflage Additional recommended
literature
Aktuelle Wirtschaftspresse
M. A. International Management 2.2 Overview: 2
ndSemester
Semester Second Semester
Modules The students choose between the following three focus modules and additionally between the following six additional modules in order to have an appropriate combination for themselves:
Focus Modules:
Marketing
Finance and Controlling
General Management of Retail Companies
Additional Modules:
Applied Business Informatics
Business Relations
Taxation
Energy Trading
Tourism-Management Number of the totally assigned
ECTS-credits
Focus Modules: 22 ECTS
Additional Modules: 8 ECTS Forms of teaching and studying of
the semester
Seminar-like Class
Working on Case Studies
Working in Groups
Working individually/ Self-Study
Overall view/Description During the second semester the students have the possibility to prepare themselves specifically for particular corporate divisions.
In order to deepen the professional expertise, the students can choose between the focus modules Marketing, Finance &
Controlling and General Management of Retail Companies.
Additionally they have to choose between the above-mentioned additional modules, which are meant to round the professional spectrum of the students.
M. A. International Management
2.2.1 Focus Module: Marketing
Module Nr. / Code 2.1
Module Designation Marketing
Semester or Trimester 2. Semester
Duration of the Module 1 Semester
Course type(compulsory, optional,
etc.) Required Elective Subject
As appropriate courses of this module 2.1.1 International Marketing
2.1.1.1 Advanced International B2B- & High Tech-Marketing 2.1.1.2 Advanced International Sales-Management
2.1.2 Retail Marketing
2.1.2.1 Strategical Marketing Planning 2.1.2.2 Operational Marketing Planning 2.1.2.3 Retail- and Consumer Behavior 2.1.3 Distribution Management 2.1.3.1 Value Innovation
2.1.3.2 Dialog-Marketing
2.1.3.3 Strategies in Direct Selling Frequency of the module offer Every Semester
Entrance requirement
None
Applicability of the Module for other courses of study
Suitable as optional subject for all international business master- studies programs
Responsible person for this module Prof. Dr. Robert de Zoeten Name of the Professor Prof. Dr. Robert de Zoeten
Prof. Dr. Joachim Theis Prof. Dr. Ralf Gampfer Contract Teachers Language of instruction German/ English Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 22 ECTS
Total workload and its composition Total Workload: 660 h Semester hours per week 15 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements for
assigning credits
See Module Description Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Qualification aims of the module The optional subject Marketing gives the opportunity to deepen the Marketing- and Sales- Knowhow on Master-level. It also allows particular specializations in the areas of Retail-, Distribution- Management, Marketing of Consumer Goods, International Sales Management as well as International B2B- and High-Tech Marketing.
The students are supposed to be able to develop practical solutions out of practice and for different initial situation and to defend those against a professional audience.
Retail-Marketing:
Particularities and processes of the strategic and operational marketing planning in the retail segment.
Imparting particular knowledge in the field of research in the retails segment connected to the latest trends and developments of the consumer behavior.
Distribution-Management:
The students are supposed to be able to critically scrutinize the marketing strategies and instruments that they have learned so far as well as to develop distribution strategies for consumer goods and services. This is based on the concepts and instruments of value innovation, dialogue marketing and multi-channel-distribution.
International Sales-Management:
The students are supposed to gain a deepened view of the modern international sales-management and its methods. Based on this knowledge they should be able to develop and implement international sales-strategy concepts by considering the practical demands. This includes the conception and management of sales- systems as well as the application of the focal sales-planning and sales-controlling-instruments.
Furthermore knowledge regarding innovative sales-methods and –tolls will be imparted.
International B2B- & High Tech-Marketing:
The student is supposed to be able to understand the specifics and market rules of the international B2B- and High Tech-markets and to develop and implement marketing concepts specifically for different business types by considering the practical demands.
Furthermore knowledge regarding innovative marketing instruments of the B2B- and High Tech-Marketing are imparted.
Imparting the specific demands of the international market engagement and its implications for market conceptions is specifically considered by the units international sales-management and international B2B- and High Tech-Marketing.
Contents of the modules See Unit Descriptions Forms of teaching and studying of the
module
See Unit Descriptions Special characteristics See Unit Descriptions Literature (compulsory reading/
additional recommended literature) See Unit Descriptions
M. A. International Management
Module: International Marketing
Module-Nr./ Code 2.1.1
Module Designation International Marketing
Semester or Trimester 2. Semester
Duration of the Module 1 Semester
Course type(compulsory, optional, etc.) Required Elective Subject
As appropriate courses of this module 2.1.1.1 Advanced International Business-to-Business- and High-Tech Marketing (International Marketing I)
2.1.1.2 Advanced International Sales-Management (International Marketing II)
Frequency of the module offer Every Semester
Entrance requirement None
Applicability of the Module for other courses of study
Suitable for all international business master studies programs
Responsible person for this module Prof. Dr. Robert de Zoeten Name of the Professor Prof. Dr. Robert de Zoeten
Language of instruction German
Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 6 ECTS Total workload and its composition (e.g.
independent study + contact time, etc.)
Total Workload: 180 h Semester hours per week 4 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements for assigning
credits10 Hausarbeit [term paper]
Weighting of the mark within the cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Qualification aims of the module Within this module the students gain a deepened knowledge regarding marketing and its particularities.
Professional Competence:
A deepened view of the discipline and practice of the international B2B- and High Tech-
Marketing
Learning to identify and understand the specific demands of international markets and
international engagement in the field of B2B- and High Tech-Marketing
10 The language in which the examination has to be completed is generally conform to the language spoken in the module.
Methodological Competence:
Learning to identify and understand
particularities of B2B- and High Tech Marketing (focus on the buying behavior and specifies of the market) by case studies and practical examples
Key Competence
Gaining the qualification to develop international B2B- and High Tech-Marketing strategies and concepts specifically for different business types
Contents of the modules See Unit DescriptionForms of teaching and studying of the module
Lecture
presentation of theory combined with subsequent practical exercises and examples of application
present independent developments of contents, Topic areas and theory as self-study and its subsequent presentation and discussion (part 1 of the examination)
Method of Case Study – Working on B2B- and High Tech- Marketing Case Studies with a subsequent presentation and discussion of the results (part 2 of the examination)
Literature per self-study Special characteristics (e.g. online-amount,
field trips, guest lecturers, etc.)
Usually one guest lecturer literature
(compulsory reading/ additional recommended literature)
See Unit Description
M. A. International Management
Unit Description of the Module: International Marketing
Code 2.1.1.1
Module Designation International Marketing
Designation of the course/unit Advanced International Business-to-Business- and High-Tech Marketing (International Marketing I)
Professor Prof. Dr. Robert de Zoeten
Language of instruction of the unit German Number of the assigned ECTS-credits 3 ECTS
Workload of this unit 90 h
Composition of the Workload Lecture: 30 h
Self-study/ preparation & follow-up of lecture: 15 h
Working on topics:: 20 h
Working on Case Studies: 25 h
Total: 90 h
Semester hours per week of the Unit 2 Semester Hours per Week Examination type/ Requirements for
assigning credits
See Module Description 2.1.1 Weighting of the mark within the
cumulative grade
According to regulations and ordinances
Contents of the unit 1. Subject and particularities of the B2B- and High Tech-Marketing 2.Organizational behavior of acquisition and approaches of
interaction
3. Conceptual level of B2B- and High Tech-marketing strategies:
The comparative cost advantage as core element 4. Marketing for particular business types
4.1 Typologies in B2B- and High Tech-Marketing 4.2 Plant Business
4.3 System Business
4.4 Classical Product Business 4.5 Commodity Business 4.6 Single Aggregate Business 4.7 Supplier Business
4.8 After-Sales-Business (Division Part / TKD) 4.9 Reseller Business (PVH - FGH)
4.10 Retail Business (B2C-directed Retailing) 4.11 Change and Dynamic of business types 5. Specific topics
5.1 Specific B2B- und High Tech-Marketing-Decisions 5.2 Pricing-Concepts in multistage markets
5.3 International Communication Strategies
5.4 Industrial Service and Rendering Service-Management 5.5 Industrial Customer Value Management
5.6 Product and Innovation Management (based on the methodology of technological topologies)
5.7 International Key Account Management