Accuracy of leg length and offset restoration in femoral pinless navigation compared to navigation using a fixed pin during total hip arthroplasty
Volltext
Abbildung
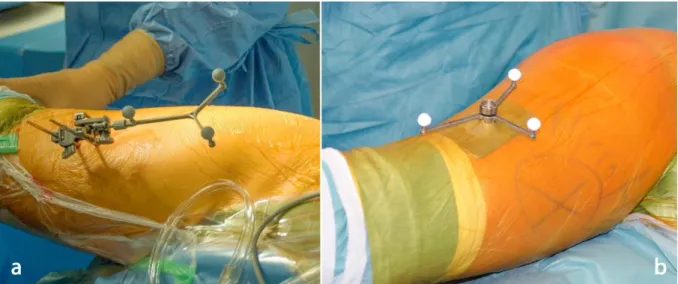
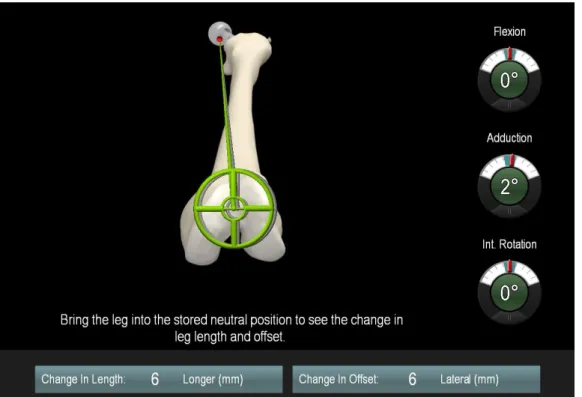
ÄHNLICHE DOKUMENTE
Factors increasing the risk of taper corrosion were identi- fied in laboratory and retrieval studies: stiffness of the stem neck, taper diameter and design, head diameter, offset,
Previous experimental research has shown that such models can account for the information processing of dimensionally described and simultaneously presented choice
For this configuration, an eigenparameter analysis of two seafloor models consisting of (1) a halfspace and (2) a resistive layer buried within a halfspace shows that the
Die Analyse gibt Aufschluss darüber, welche Faktoren relevant sind, wenn eine obli- gatorische Kommaposition als solche wahrgenommen, also ‚bedient‘ wird oder nicht.. Innovativ
[2] eine Tenotomie vorgenommen, die in 3 Fällen zu einer vollständigen und in 1 Fall zu einer partiellen Beschwerde.
As shown in Figure 3, scan points which belong to a landmark, do not represent the surface’s curvature due to the de- pendence of the laser scanner range measurement error on the
The BSH is thus not only responsible for the approval of offshore wind farms, the supervision of their construction, but also for the development of offshore grid plans for the
Results from these studies indicate that core-scale and formation-scale permeability values differ by at least several orders of magnitude and are depen- dent on pore-fluid pressure