Some studies for a development of a small animal PET based on LYSO crystals and Geigermode-APDs
E. Lorenz
a),b),d)1, I. Britvich
b),c), D. Ferenc
d), N. Otte
a), D. Renker
c), Z. Sadygov
e), A. Stoykov
c)a)
Max Planck Inst. for Physics, Foehringer Ring 6, D 80805 Munich, Germany
b)
ETH Zurich, Hoengger Berg, Schafmattenstr., CH 8093. Zurich, Switzerland
c)
Paul Scherrer Institute, CH 5233 Villigen Switzerland
d)
Physics Dep. UC-DAVIS, One Shield Av, Davis, CA 95616-8677 USA
e)Joint Institute for Nuclear research, 141980 Dubna, Russia
Abstract
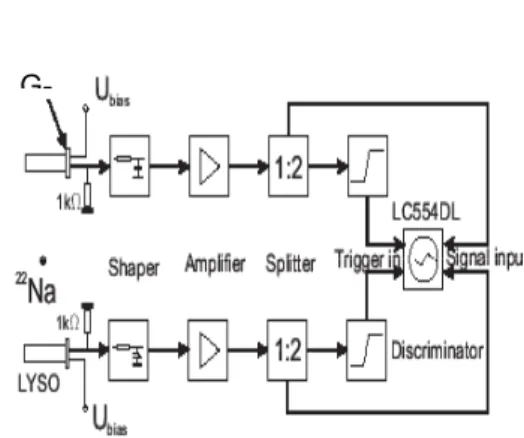
The use of Geiger Mode APDs (G-APD)/micro-cell APDs (MAPD) opens new simplifications in PET designs. We report on some test studies for a Small Animal PET based on LYSO crystals and G-APDs/MAPDs for readout. Emphasis is put on time and energy resolution.
Keywords: PET detector; Geigermode Avalanche Photodiodes
____________________________________________________________________________________________________
1