Worksheet 14
4. Acids and Bases/Alkali
Acids
Originally the word acid was applied to substances with a sour taste, e.g. vinegar. The acids present in animals and plants are known as organic acids. Chemically speaking acids are substances that, when dissolved in water, produce an acidic solution containing H+-ions.
Some acids are comparatively weak or diluted, for example the phosphoric acid in cola.
Other acids are strong or concentrated, for example the sulfuric acid in a car battery. High concentrations of H+-ions in an acidic solution, caused by a strong or highly concentrated acid, are corrosive, meaning they damage or destroy other materials they come in contact with.
Base/Alkali
A substance that neutralizes an acid (removing H+-ions from the solution). Chemically speaking bases produce OH--Ions when dissolved in water, creating an alkaline solution.
While the corrosive nature of acids is feared, strong or concentrated bases are also corrosive and can cause terrible damage to living tissue, for example an eye.
Indicators
Indicators are substances that change color if they are put into an acidic or an alkaline solution.
The most common indicator is litmus (acid red / base blue).
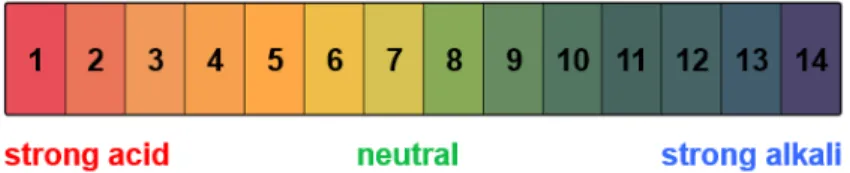
The pH scale
The pH scale gives an indication of how acidic or alkaline a solution is (by stating the
concentration of H+- and OH--Ions). A neutral solution is neither acidic nor alkaline and has a pH of 7. A pH value lower than 7 means a solution is acidic, a pH value higher than 7 means a solution is alkaline. The further away from 7 the pH value is, the stronger the acidic or alkaline solution.
Questions
a) When dissolving an acid, such as HCl (hydrogen chloride), in water it forms an acidic solution. While both water and HCl are neutral molecules the acidic solution contains a high amount of ions. Set up the chemical equation to explain.
b) The neutralization reaction happens when an acidic solution is mixed with an alkaline solution. Use the information above to write a chemical equation for the
neutralization reaction.
c) A base produces OH--ions by reacting with water molecules in an alkaline solution.
Use this information to explain, why bases are the exact opposite of acids!
Figure 1: The pH scale and the corresponding color of universal indicator solution
Worksheet 14 Experiment: pH values of everyday substances
a) Complete the table to determine if common household substances are acidic or alkaline solutions and what their pH is.
Item Acid or Base
Litmus test
pH (using pH-meter or universal
indicator) Milk
Water Vinegar Yogurt Natural soap Dish washing detergent
Baking soda solution
b) Red cabbage juice is a natural indicator. Use the table above to note the color of red cabbage juice at the different pH values.
Questions
1. Why is natural soap today not used as often as artificial detergents?
2. Describe the following solutions by their respective pH values a. pH =11
b. pH = 7 c. pH = 3 d. pH = 6
3. Name an element that all acid molecules contain.