Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - N e w Crystal Structures 212, 4 0 1 - 4 0 2 4 0 1 by R. Oldenbourg Verlag, M ü n c h e n 1997
Crystal structure of trimethylamine-hydrogen chloride (2/3), [(Me 3 NH) 2 Cl][HCl 2 ]
A. Deeg, Th. Dahlems and D. Mootz
Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf. Institut für Anorganische Chemie und Strukturchemie. Universitätsstr. I. D-40225 Düsseldorf. Germany Received November 6. 1996. CSD-No. 402690
Table 1. Parameters used for the X-ray data collection
C I 3
H 3 CI2
Source of material: The title compound, melting point 3 0 2 K, has been identified, along with six others, in a melting-diagram study o f the underlying amine-hydrohalide quasi-binary system (see ref.
1).
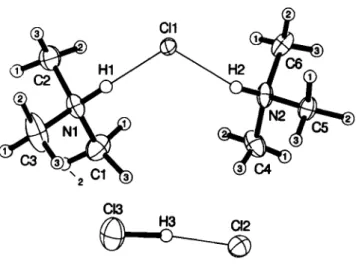
Crystal structures for a 1/1 and a 1/3 adduct, both ionic, have already been reported (see refs. 2-4). The 2/3 adduct o f the present study is also ionic. T w o independent trimethylammonium cations e x t e n d an N - H - - C 1 h y d r o g e n b o n d e a c h (N--C1 d i s t a n c e s 3.099(3) À and 3.088(3) Â ) to a c o m m o n chloride anion. This ionic triad and higher complexed cation is then opposed by a hydrogen-dichloride anion ( C l - C l 3.136(2) Â).
C6H21CI3N2, monoclinic, P 1 2 i 1 (No. 4), a =5.378(2) À,
¿>=10.383(4) A, c =11.316(4) Â, ß=91.72(3)°, V = 6 3 1 . 6 Â3, Z = 2 , R(F) =0.044, R*(F) =0.050.
Crystal: colorless, grown from the melt, radius 0.1 mm Wavelength: Mo Ka radiation (0.71073 Â)
μ: 6.9 cm"1
Diffractometer: Syntex P21
Scan mode: ω
Τ measurement'· 123 Κ
26max: 65°
N(hkl)u„ique: 2024 Criterion for /0: A, > 2 σ(/0)
Ν (param),efi„ed·· 183
Program: SHELXTL-plus
Table 2. Final atomic coordinates and displacement parameters (in À2)
Atom Site X y ζ l/iso
H(l) 2a 0.111(9) 0.473(6) 0.706(4) 0.05(1) H(2) 2a 0.119(8) 0.673(5) 0.912(4) 0.02(1) H(3) 2a 0.46(1) -0.031(7) 0.678(6) 0.08(2) H ( l l ) 2a -0.28(1) 0.565(7) 0.683(5) 0.06(2) H(12) 2a -0.28(1) 0.542(6) 0.532(5) 0.05(1) H(13) 2a -0.07(1) 0.660(7) 0.613(5) 0.06(2) H(21) 2a -0.211(9) 0.310(6) 0.585(5) 0.05(1) H(22) 2a -0.227(8) 0.366(5) 0.719(4) 0.03(1) H(23) 2a 0.03(1) 0.277(8) 0.668(6) 0.08(2) H(31) 2a 0.084(8) 0.432(5) 0.457(4) 0.02(1) H(32) 2a 0.31(1) 0.363(6) 0.552(5) 0.05(1) H(33) 2a 0.261(9) 0.530(6) 0.523(4) 0.05(1) H(41) 2a -0.232(7) 0.867(5) 0.894(4) 0.02(1) H(42) 2a -0.283(9) 0.735(6) 0.829(4) 0.04(1) H(43) 2a -0.054(7) 0.818(5) 0.806(3) 0.02(1) H(51) 2a 0.345(8) 0.768(5) 1.045(4) 0.03(1) H(52) 2a 0.147(7) 0.899(4) 1.047(3) 0.01(1) H(53) 2a 0.304(8) 0.856(5) 0.934(4) 0.03(1) H(61) 2a -0.231(7) 0.621(5) 1.012(4) 0.02(1) H(62) 2a 0.008(7) 0.629(4) 1.096(4) 0.02(1) H(63) 2a -0.201(8) 0.734(5) 1.091(4) 0.02(1)
Table 3. Final atomic coordinates and displacement parameters (in Â2)
Atom Site X y ζ υ h t/22 t/33 (/|2 Un ί/23
Cl(l) 2a 0.3339(1) 1/2" 0.8599(1) 0.0209(3) 0.0157(3) 0.0174(3) 0.0037(3) -0.0018(2) -0.0007(3) Cl(2) 2a 0.3586(2) -0.1930(1) 0.6506(1) 0.0277(4) 0.0319(4) 0.0240(3) -0.0018(4) -0.0023(3) 0.0049(4) Cl(3) 2a 0.4878(2) 0.0900(1) 0.7274(1) 0.0591(7) 0.0376(6) 0.0431(6) -0.0050(5) 0.0111(5) -0.0108(5) N(l) 2a 0.0146(5) 0.4603(3) 0.6302(2) 0.023(1) 0.035(2) 0.019(1) 0.000(1) -0.001(1) -0.005(1) N(2) 2a 0.0283(5) 0.7311(3) 0.9474(3) 0.016(1) 0.026(2) 0.025(1) 0.004(1) 0.000(1) -0.011(1) C(l) 2a -0.1669(8) 0.5662(4) 0.6088(4) 0.032(2) 0.030(2) 0.046(2) 0.000(2) -0.008(2) -0.003(2)
a: arbitrarily fixed for definition of the origin
402 Trimethylamine-hydrogen chloride (2/3)
Table 3. (Continued)
Atom Site X y ζ U,, Un t/33 Un U13 t/23
C(2) 2a -0.1152(8) 0.3380(4) 0.6555(4) 0.046(2) 0.033(2) 0.030(2) -0.004(2) -0.009(2) -0.004(2) C(3) 2a 0.1856(8) 0.4462(7) 0.5319(4) 0.029(2) 0.089(4) 0.034(2) -0.014(2) 0.007(2) -0.026(2) C(4) 2a -0.1448(6) 0.7995(5) 0.8642(3) 0.026(2) 0.047(2) 0.023(2) 0.008(2) -0.003(1) -0.006(2) C(5) 2a 0.2247(6) 0.8187(4) 0.9965(3) 0.019(1) 0.023(2) 0.032(2) -0.005(1) 0.000(1) -0.008(1) C(6) 2a -0.1104(7) 0.6712(4) 1.0454(4) 0.023(2) 0.019(2) 0.045(2) -0.001(1) 0.000(2) -0.005(2)
Acknowledgments. Support by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Fonds der Chemischen Industrie and Dr. Jost Henkel-Stiftung is gratefully acknow- leged.
References
1. Deeg, Α.: Ionische und molekulare Addukte mit Chlorwasserstoff: Bildung, Kristallstruktur, Wasserstoffbriickenbindung. Dissertation, Universität Düsseldorf, Germany 1992.
2. Stammler, M.: Polymorphism of Salts Containing Complex Ions I. The Halides of Ammonium and Methyl-Substituted Ammonium. J. Inorg.
Nucl. Chem. 29 (1967) 2203.
3. Lindgren, J.; Olovsson, I.: Hydrogen Bond Studies XVIII. The Crystal Structure of Trimethylammonium Chloride. Acta Crystallogr. B24 (1968) 554.
4. Mootz, D.; Hocken, J.: Anion Coordination and Cl-H CI Bridges in the Low-melting Poly(Hydrogen Chloride) Me3N - 5HC1. Angew. Chem. Int.
Ed. Engl. 28 (1989) 1697.
5. Sheldrick, G. M.: Program Package SHELXTL-plus. Release 4.11. Siemens Analytical X-Ray Instruments Inc., Madison (WI53719), USA 1990.