Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome – a multidisciplinary collaboration
Streptokokken induziertes toxisches Schock-Syndrom – eine interdisziplinäre Herausforderung
Eva Weidenbach
1Julia Sproedt
1Abdul Rahman Jandali
1Florian Jung
11 Kantonsspital Winterthur, Switzerland
Introduction
Severe group A streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS) has generally a poor outcome. Patients present a life- threatening toxic shock syndrome within hours resulting from a harmful injury or infection with beta-hemolytic streptococci. The fast progression will lead to the death unless prompt supportive and aggressive treatment.
There are only a few cases published in literature and mostly only case reports.
Material and methods
We report 3 cases of previously immune-competent, 41- to 76-year-old, male patients. The hospitalisation took place during 2012 and 2014. The referral to our acute interdisciplinary center was made for further treatment of suspected necrotizing fasciitis. Diagnosis included a combination of laboratory, imaging modalities and histo- logical analysis. The patients were healthy and did not suffer any chronical condition. Initially started antibiotic therapy was in the course matched to the infectiological results. All surgical intervention was led by our plastic- surgeon-team.
Results
All patients had to have an intensive care support be- cause of their serious condition with mechanical ventila- tion and monitoring. The average stay at the intensive care unit was 20 days, the hospital stay took on average 57 days. The improvement of the physical condition was made by rapidly initiated antibiotic treatment and imme-
diate aggressive surgery. CT scan was initiated with two patients who had an unknown focus of infection.
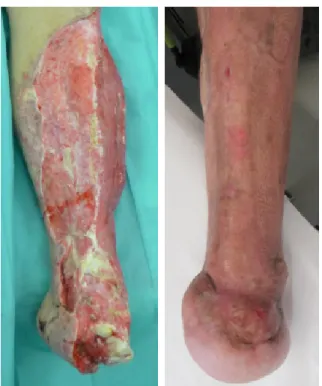
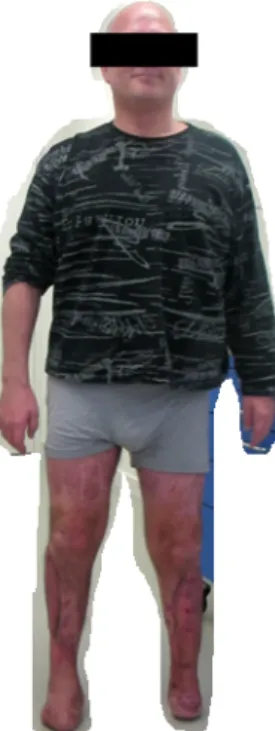
Patient 1 suffered from a peripharyngeal abscess which was shown on the CT scan. He developed a severe gen- eral state of health and a progressive soft tissue destruc- tion due to the peripharyngeal abscess. Involving an ENT doctor was needed for resection of the palatine tonsils and the abscess cavity. Furthermore this patient had to undergo partial amputation of the lisfranc-joint at both lower legs. For preventing functional movement we per- formed a Pirogoff-amputation on one forefoot with the assistance of orthopedic specialists from the university hospital Balgrist/Zurich. On the other forefoot we per- formed a free Gracilis-flap. Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the clinical findings pre-/peri and postoperative of patient 1.
The other patient (Patient 2) with unknown focus showed in the course a portal of entry on the hand. He suffered a severe hyperactive delirium due to a chronic alcohol abuse. Therefore we could not obtain a medical history.
The third patient (Patient 3) got a known sharp cut on the palm by a metal plate. He suffered a necrotizing fasciitis with a septical state of health within 24 hours after injury.
All patients had to undergo on average 8 surgical inter- ventions with debridement on the particular extremities.
Successful outcome was possible provided by a mul- tidisciplinary, intensive and continuous both conservative and surgical therapy in close collaboration [1].
1/3 GMS German Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery 2016, Vol. 6, ISSN 2193-7052
Extended Abstract
OPEN ACCESS
Best Abstract Award DGPRÄC 2015
Figure 1: Admission findings
Figure 2: Debridement after forefoot amputation
Figure 3: Stump care with ALT-flap after 2 months
Figure 4: Stump care with tibiocalcaneal arthrodesis
Figure 5: X-ray 1+2: stump care with tibiocalcaneal arthrodesis
2/3 GMS German Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery 2016, Vol. 6, ISSN 2193-7052
Weidenbach et al.: Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome – a multidisciplinary ...
Figure 6: Result with a standing/walking patient 1 after successfully treatment
Conclusion
STSS is a rare described condition and to our knowledge no evidence based medical guideline is known. The sur- vival of the life-threatened bacteriosis is only warranted by rapid therapy of an experienced team by plastic sur- geons, infectiologists, intensive-care physicians and other surgical discipline. As soon as the critical condition passed the team has to be extended by nutrition counseling, psychiatrists, physio- and occupational therapists. Togeth- er with this extensive collaboration the best outcome will be required. Long stay at the hospital with multiple sur- geries and a subsequent long-term rehabilitation provide a sufficient recovery and a successful therapy.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing in- terests.
Note
At the 46thmeeting of the German Society of Plastic, Re- constructive and Aesthetic Surgeons (DGPRÄC) the cor- responding abstract [2] was awarded “Best Abstract”.
The society highlighted the best abstract submissions with this award in 2015. The publication of the extended abstract in GMS German Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery – Burn and Hand Surgery was sponsored by “Amryt Pharma”.
References
1. den Bakker FM, Holtslag HR, van den Brand JG. Pirogoff amputation for foot trauma: an unusual amputation level: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 Oct 20;92(14):2462-5. DOI:
10.2106/JBJS.I.01336
2. Weidenbach E, Sproedt J, Jandali AR, Jung F. Streptokokken- induziertes toxisches Schock-Syndrom, eine interdisziplinäre Herausforderung. In: 46. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft der Plastischen, Rekonstruktiven und Ästhetischen Chirurgen (DGPRÄC), 20. Jahrestagung der Vereinigung der Deutschen Ästhetisch-Plastischen Chirurgen (VDÄPC); 2015 Oct 1-3; Berlin. Düsseldorf: German Medical Science GMS Publishing House; 2015. Doc062. DOI: 10.3205/15dgpraec062
Corresponding author:
Eva Weidenbach
Kantonsspital Winterthur, Brauerstrasse 15, 8401 Winterthur, Switzerland
eva.weidenbach@ksw.ch
Please cite as
Weidenbach E, Sproedt J, Jandali AR, Jung F. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome – a multidisciplinary collaboration. GMS Ger Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;6:Doc08.
DOI: 10.3205/gpras000043, URN: urn:nbn:de:0183-gpras0000431
This article is freely available from
http://www.egms.de/en/journals/gpras/2016-6/gpras000043.shtml Published:2016-09-29
Copyright
©2016 Weidenbach et al. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. See license information at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
3/3 GMS German Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery 2016, Vol. 6, ISSN 2193-7052
Weidenbach et al.: Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome – a multidisciplinary ...