Ζ. Kristallogr. NCS 217 (2002) 483-484 483
© by Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, München
Crystal structure of the cate/ia-pentelides KAs and Na(Aso.sSbo.s)
W. Hönle*·
1, J. Buresch
11, K. Peters", J. H. Chang" and H. G. von Schnering"
1 Max-Planck-Institut für Chemische Physik fester Stoffe, Nöthnitzer Str. 40, D-01187 Dresden, Germany
" Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Heisenbergstr. 1, D-70569 Stuttgart, Germany
Received September 17, 2002, accepted and available on-line November 5, 2002; CSD-No. 409653 and 409654
Na(As
0.5Sb
0.5)
2 . 4- 1
kJ ft
CL
2 . 2 -
2 . 0 -
LiAs-type
Sb"
Na(As
0,Sb
0,) • NaP-type
• As"
0.5
Li Na'
-ι 1 r-
1.0 +
i s R ^ y A
K+ Rb+ Cs+
Abstract
AsK, orthorhombic, P2\2\2\ (No. 19), a = 6.681(2) Â, b = 6.425(2) Â, c = 11.602(3) Â, V = 498.0 Â
3, Ζ = 8,
R
&(F) = 0.029, wRretfF
2) = 0.076, T= 293 K.
Aso.5NaSbo.5, monoclinic, P12i/cl (No. 14), a = 6.404(3) Â, b = 6.046(2) Â, c = 11.853(4) k,ß= 117.05(2)°, V= 408.7 Â
3, Z= 8, Rgt(F) = 0.065, wRrtfiF
2) = 0.128, Τ =293 Κ.
Source of material
Pure KAs was synthesized from stoichiometric mixtures of the elements in welded Nb tubes ( 12 h up to 900 K, 48 h at 900 K, 36 h down to 298 K; single crystals from Pb-melts under same condi- tions with K: As:Pb = 2:2:1 ) [ 1,2]. KAs forms dark-grey prismatic needles with metallic lustre (very sensitive for hydrolysis).
Na(Aso.sSbo.5) was formed as by-product of syntheses of mixed heptaarsenides [2] (grey platelets with metallic lustre; sensitive for hydrolysis).
Discussion
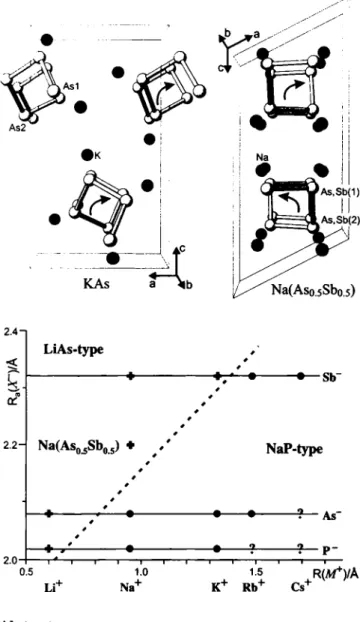
KAs is isotypic to NaP, whereas Na(Aso¿Sbos) crystallizes in the LiAs type of structure. In both types, the main structural features are l [ i n helices of (2b)X" anions which are fully according to the Zintl concept. In KAs, these helices have the same rotation sense, in Na(Aso.sSbo.s) they are rotated anticlockwise (see upper figure). The bond lengths d(X~—X~) are d(As—As) = 2.482(1) Â and 2.499(1) Â, d(As/Sb—As/Sb) = 2.588(2) À and 2.610(2) Â, corresponding to typical single bond distances X~—X~. In Na(Aso.sSbo.s), the As and Sb atoms show a preferred occupancy for the crystallographic atom sites X(l) and X(2), respectively.
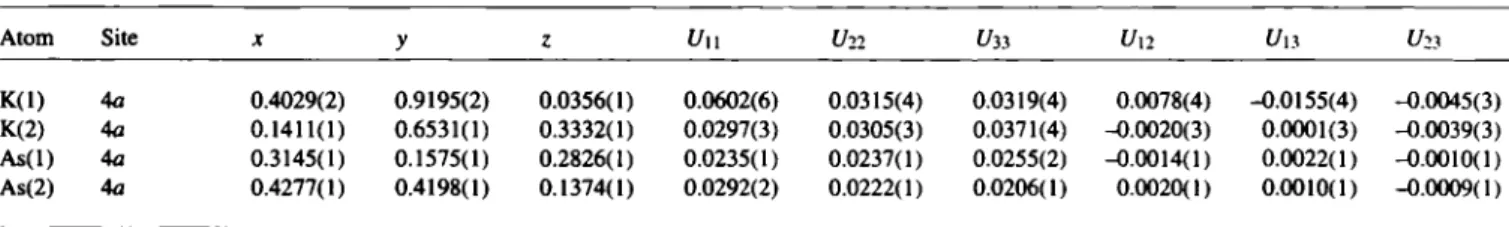
The two structure types NaP and LiAs can be separated [3] with respect to ionic radii R(M*) and Ra(X~) according to Klemm [4].
The existence of Na(Aso.sSbo.5) in the LiAs type of structure sup- ports the chosen separation between the two structure types (see lower figure).
1. The catena-pentelide KAs
Table 1. Data collection and handling.
Crystal: dark-grey prismatic needle, size 0.1 χ 0.1 χ 0.4 mm Wavelength: Mo Ka radiation (0.71073 Â)
148.91 cm!1
Diffractometer, scan mode: Siemens PI, ω 70°
^AWjmeasiuK), N(hkl)mique: 2191,2191 Criterion for /obs, N(hkl) /obs > 2 CTf/obsJ, 2091 N(param)refined: 38
Programs: SHELXL-97 [5], ATOMS [6]
* Correspondence author (e-mail: hoenle@cpfs.mpg.de)
484
The ca/ewa-pentelides KAs and Na(Aso.5Sbo.5>Table 2. Atomic coordinates and displacement parameters (in Â2).
Atom Site l/u U22 Un f/12 υ υ Uz:
K(l) 4a 0.4029(2) 0.9195(2) 0.0356(1) 0.0602(6) 0.0315(4) 0.0319(4) 0.0078(4) -0.0155(4) -0.0045(3) K(2) 4a 0.1411(1) 0.6531(1) 0.3332(1) 0.0297(3) 0.0305(3) 0.0371(4) -0.0020(3) 0.0001(3) -0.0039(3) As(l) 4a 0.3145(1) 0.1575(1) 0.2826(1) 0.0235(1) 0.0237(1) 0.0255(2) -0.0014(1) 0.0022(1) -0.0010(1) As(2) 4a 0.4277(1) 0.4198(1) 0.1374(1) 0.0292(2) 0.0222(1) 0.0206(1) 0.0020(1) 0.0010(1) -0.0009(1)
2. The cateiia-pentelide Na(Aso.sSbo.s)
Table 3. Data collection and handling.
Crystal:
Wavelength:
μ·
Diffractometer, scan mode:
IBjsax.
WfAWJmeasured, WfAWVique:
Criterion for /obs, N(hkl)ρ: Nfparam^fwcd:
Programs:
grey platelet, size 0.05 χ 0.15 χ 0.2 mm Mo Ka radiation (0.71073 Â)
292.73 cm"1 Siemens P4, ω 55°
940,940 /obs > 2 CTf/obs), 725 40
SHELXL-97 [5], ATOMS [6]
Table 4. Atomic coordinates and displacement parameters (in Â2).
Atom Site U11 U22 Í/33 U12 U13 U2)
Na(l) 4e 0.214(1) 0.396(1) 0.3272(5) 0.039(4) 0.043(4) 0.034(4) -0.003(3) Na(2) 4e 0.241(1) 0.662(1) 0.0331(5) 0.046(4) 0.034(4) 0.034(3) -0.001(3) XU)" 4e 0.3166(2) 0.8928(2) 0.2912(1) 0.0332(9) 0.0344(8) 0.0353(9) -0.0011(6) X(2)b 4e 0.3034(2) 0.1588(2) 0.1147(1) 0.0337(7) 0.0283(6) 0.0273(6) 0.0037(5)
0.019(3) -0.008(3) 0.018(3) -0.005(3) 0.0204(7) -0.0024(6) 0.0145(5) -0.0011(5) a:X(l) = 0.69(4)As + 0.31Sb
b: X(2) = 0.33(5)As + 0.67Sb
Acknowledgment. Thanks are due to W. Giering (Stuttgart) for help with the sample preparation.
References
1. Hönle, W.: Über niedere Phosphide, Arsenide und Antimonide der Alkalimetalle, Dissertation, Universität Münster, 1975.
2. Buresch, J.: Binäre und ternäre Arsenide, Antimonide und Arsenid- Antimonide der Alkalimetalle mit den Anionen Χ3", X35", X45-, 1[Χ~], X71" und X75". Dissertation, Universität Stuttgart, 1996.
3. von Schnering, H. G.; Hönle, W.: Darstellung, Strukturen und Eigenschaften der Alkalimetallmonophosphide NaP und KP. Z. Anorg.
Allg. Chem. 456 (1979) 191-206.
4. Klemm, W.; Busmann, E.: Volumeninkremente und Radien einiger einfach negativ geladener Ionen. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 319 (1963) 297-311.
5. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXL-97. Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structures. University of Göttingen, Germany 1997.
6. Dowty, E: ATOMS 5.1. A Complete Program for Displaying Atomic Structures. By Shape software, 521 Hidden Valley Road, Kingsport, TN 37663, USA 2000.