Kongreß für Laboratoriumsmedizin 1998
^^ . . . .-..·, . · " · ./Jy·-' v" - · · . - · '·> : ·:' V \^JJia^:c->.Ä^.Wi?.v,,rt«fder Deutschen Gesellschaft für Laboratoriumsmedizin und der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Klinische Chemie
Kongreßpräsident M. Krieg
Wissenschaftlicher Beirat
G. Assmann, T. Deufel, W. Ehret, R da Fonseca-Wollheim, A.M. Gressner, E. Köttgen, M. Krieg, J. D. Kruse-Jarres, D. Meißner, J. Muche, H. Patscheke, H. Reinauer,
H. Rodt, G..Schumann, L Thomas, C. Wagener
Düsseldorf; 15. - 18. November 1998
1 Abdruck der Abstracts nach den von den Autoren eingereichten Vorlagen, ohne redaktionelle Bearbeitung
Autorenverzeichnis
Adler. G 651,652 AI-Fakhri. N 659 Althaus, II 648,664 Armbnistcr. F.P. 649 Armstrong. V.W. 683 Arsicf, T. 661 Assmann, G 660, 671 Bachern, M.G. . . . 645, 651. 652, 655, 656 Baller, D 659 Barlage, S 656 Barnard, K 682 Bauer, Th 679 Becker, W. 641 Beckmann, M.W. 649 Beicr. L 665 Berendes, B 671 Berndt, Ch 669 Bidlingmaier, F. 676 Birkl, J 640 Bodis, M 675 Bönsch, D. 672 Börner, A 657 Borncr, E 684 Borner, K 684 Borries, M 658 Bosse. S 645 Böttcher, A 656 Braun, Chr. 678 Brinkmann, K 666 Brinkmann, T. 643, 650, 651, 659 Bülow, J.v ". 666 Capelle, H.H 669 Celik, E 655 Chari, S 679 Debus, N 647 Deuber, H.J. ·. 664 Deufel, Th 657, 662, 671, 672 Dickerhoff, R 644 Diekmann, J 659 Dierkes, J 660 Dooley, S 652, 674 Doss, M.0 640 Druschky, K.-F. 641 Drzeriiek, Z 646 Eberle, A 673 Ebert, W. 668 Ehrich, J.H.H 666 Eigenbrodt, E 670 Eisenbrandt, H 666 Eller, Th '.640 Emig-Vollmer, S 647 Engel, A 672 Erren, M 671 Faber, R ' 683 Fabricius, H.-Ä .· 641, 647 Fiedler, M 673 Fieger, C 647 Fischer, Y. 657, 658 Fitzner, R 666 Flemming, P. 677 Fluit, A.C 679 Fröhlich, D 656 Fuchs, H 672 Funke, H 660
Gao, Q 680
Gardemann. A 660, 661 Gartung, C 653, 673 Gehrisch. S 653, 654 Geisel. J 675 Geßncr. R 672, 674 Giffhorn-Katz, S 677 Gleichmann, U 642, 659 Gleixncr, J. > 643 Golf, S 680 Gondolf, M 679 Götting, C 643, 650, 651 Grabensee, B 650 Grau, A 641 Gräßler, J 663, 675 Gressner, A.M 652, 653, 673, 674 Grill, C 662 Gross, H.J 645, 651, 652, 656 Groß, W. 656 Gruber, W. 664 Grünert, A. . 645, 651, 652, 655, 656, 662, Guder, W.G 654, 666, 671663 Günnel, Th 647 Haberbosch, W. 660, 661 Hampel, R 649 Mansch, S 649 Hardy, J : ... 680 Harms, E 662 Harthus, H.-P. 648, 664, 680 Haubeck, H.-D 646 Haug, C 656, 662, 663 Hauss, J 645 Hehrlein, F.W. 659, 660, 661 Heidrich, J.P. 679 Heidt, M · 659 Heins, M 657, 658 Heinz, H.-P. 679 Heitmann, B 677 Herrmann, W. 664, 675 Heyne, B 654 Hillebrand, T. 669 Hinney, K 643 Hofmann, W. 654, 671 Huang, B 659.
Huerkamp, C 650 Hütter, G 678 Immenschuh, S 677 Ivandic, M 654, 666, 671 - Jaroß, W. 653, 654, 656, 682 Jehle, P.M .' 662 Jöchle, W. 663 Jung, R 669 Just, U 646 Jüttler, E · 64~1 Kaestner, U. . 671 Käferstein, R 641 Kage, A 678 Karmatschek, M ' 649 Katz, N 659, 660, 661, 677, 680 Keller, F. 643 Kiehntopf, M 662 Kießig, S.T. . . 664 Kleesiek, K 642, 643, 650, 651, 659 Kleist, S 649
Kleophas, W. 663 Klingcr. G 657 Klingmüller, D 676 Koch, H.G 662 Koenig, S 649 Koeppe, P. 684 Köhler, S 665 Kohlhaw, K 645 Kona-Horstmann, M 669 Konowski, Chr. 654 Kopprasch, S 663, 675 Köttgen, E 669, 674, 678, 681 Kramer, W. 670 Kraul, D. - 648, 680 Kreft, S. ..·. 641,642 Krieg, M 676 Krieg, T. 650 Kröpf, J 640 Kruempelbeck, G 649 Krüger, W. 669 Kruse-Jarres, J.D 653 Kuhn,J 650,651 Kühne, H 675 Kurz, J 640 Labeit, D 668 Lackner, K.J 644 Ladusch, M 645 Lage, H 678 Lahme, B 653 Lammers, M 648, 664 Lamprecht-Dinnesen, A 672 Landenberg, C.v 644 Landenberg, P.v 644 Langer, E 666 Läßner, D 645 Lehmann, J 659 Leschke, M 657, 658 Leur, E. van de 653 Lieben, U.G 645 Litfin, F. 641, 642 Lode, H .684 Lotterie, H 668 Lücken; U 672 Luft, JF.C 674 Luley, C 660 Lun, A 665, 666, 681 Luttenberger, T. 651. 652 Mages, P. 661 Mahley, R.W. 660 Mangasser-Stephan, K 652, 674 Mannebach, H 642 Markau, S 664 Melchert, F. 668 Menke,A 651,652 Merie, P. 680 , 670 Mothes, Th 647 Nauck,M 660 Neumaier, M 669 Neumann, C 672 Neuss, H 669 Niederau, C 657, 658 Niedmann, P.D ."683 Niemeier, A 679 Nietzschmann, U 657 Noll, B 674
Nollau, P. 669 Nuck, R 678 Nüssler, A 656 Oellerich, M. 655, 674, 683 Ohlmann, A ' 677 Ommert, S . . : 656 Oremek, G.M 670 Orth, M 660 Osman, A.A 647 Osten, B 664 Ostertag, W. 646 Özel, M 678 Paar, D 640 Paeizold, A 663 Parpart, B 663 Pasutto, F. 671 Paischeke, H. . 641, 642 Paul, M 659 Pauli, G 678 Pausner, N 650 Perlitz, Chr. 678 Petersen, K 669 Pfeufer, A 674 Philipp, M 659, 660 Plecko, Th ·. 653 Pollok, R 655 Priem, R 665, 666 Prohaska, W. '. 642, 643 Pustowoit, B 645 Quast, S 664 Quinzio, L 648 Rabilloud, Th 678 Reichmann, H 682 Reinauer, H 657, 658 Remke, H 645 Reuner, K.H 641, 642 Reutter, W. 678 Rickmann, H 641 Riegel, W. 664 Rogge, Th 647 Roggendorf, M 673 Rohe, M 662, 671 Rokos, K 678 ROSS, R.S 673 Rotn-Eichhorn, S. . 677 Rothe, G 656 Rücker, A.v. V 644 Ruf, A 641,642
Ruf, J 669
Rükgauer, M — 653 Rust, S 671
Salomon, A 678 Schambeck, C.M 643 Schanzenbächer, U 668 Scheele, J 668 Scheer, P. 672 Schickel, J 662, 671 Schilling, A 671 Schlauerer, K 666 Schlüter, B ' 671 Schmid-Kotsas, A. 645, 651, 652, 656, 662 Schmidt, B 648 Schmidt, M. . . : 642, 643 Schmilz, B 653 Schmilz, F.-J 679 Schmilz, G 644, 656 Schmilz, U 654, 671 Schneider, E 651 Schneider, l 664 Schneider, J 670 Schneider-Mergener, J 647 Schoebel, F.C 658 Schramm, J 676 Schröder, H.-E 663, 675 Schubert, K 657 Schuff-Werner, P. 649, 655 Schuster, H 674 Schütz, E 674, 683 Schwartz-Albiez, R 645 Schwarz, R 645.
Semmler, W. 647 Shipkova, M 683 Shoolian, E 678 Siebertz, B 646 Siech, M 651 Siegert, M 682 Siekmeier, R 656, 682 Sinha, P. 665. 669, 678, 681 Sollberg, S 650 Sommer, St 641 Spiteller, G 657 Springer, W. 644 Stachon, A 676 Stamminger, G 665 Sleinbach, G 662. 663 Sleinmetz, A *. . . 660, 674 Stief, T.W. 640 Stiegler,-H 657, 658 Stöcker, G 646 Stoffel-Wagner, B 676 Stolz, E " 641 Slorch, P. 672 Sireck, S 668 Stricker, J 661 Siurm, G... 679 Stürzenhofecker, B 674
Sudbrak, R 671
Tag, C 652, 674
Tauber, R 647, 672 Tersteegen, B 663 Tiebel, 0 653 Tillmanns, H 660, 661 Tolh, T 664, 680 Traulwein, C 677 Trendelenburg, Chr. 683 Uhlig, H 647 Usadel, K.-H 670 Velcovsky, H.-G \ 670 Verhoef, J 679 Viazov, S 673 Vlaskou, D. 654 Vogl, J 655 Volz, B 647 Wagener, C 669 Wagner, 0 645 Walter, G 648 Walz, T. 675 Watzka, M 676 Weidemann, H 660 Weise, R 659 Weisgraber, K.H 660 Weisheil, R 680 Weisser, H 676 Wendelin, D 656 Weng, W. 660 Wennauer, R 655 Wenzke, M 645 Werle, B. . ,. 668 Wieland, E 655, 683 Wieland, H 660 Winnefeld, K 657, 668 Withold, W. 649, 650 Will, H 674 Wolf, M 669 Woller, K ..664 Wormek, A 683 Zander, A 669 Ziebig, R 665,681 Ziegler, Ch 663 Ziemssen, T. 676 Zieren, J 669 Zingler, C 649 Zorn, U 655, 656, 663
A-1
A specific functional assay for soluble fibrin polymers in plasma
T.W. Stier, J. Kurz*, J. Birkl*. J. Kröpf*, M.O. Doss*
' Institute for Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital of Philipps University, Marburg
There is clinical nccd for sensitive assays that detect hcmo- stasis aclivation. Fibrin äs thc cnd proüuct of coagulation can occur in plasma in a soluble form. The determination of ihis substance facilitates the clinician to diagnosc a possible prethrombotic state or a disseminaled intravascular coagula- tion (DIC). We have devcloped a functional test for soluble fibrin polymers (SFP) based on its t-PA stimulatory action.
Addition of 74 mmol/l (final assay concentration) of argi- nine rcsults in high specificity for SFP, since related sub- stances such äs the natural ones D- Dinier, X- oligomer, fragment Y, or the synthetic one BrCN-cleaved fibrinogen (that all stimulate t-PA in absence of free arginine) do not enhance t-PA activity in presence of free arginine. The argi- nine added inhibits protein/protein interactions, dissociating the noncovalently linked fibrin(ogen) derivatives, but it does not inhibit the action of the covalently connected SFP. The pipetting scheine for this new assay is:
25 l Plasma (citrate or EDTA)
25 l Plasminogen reagent (0.4 mg plasminogen/ ml in 1.25% PEG, 190 mmol/l arginine)
25 l Taurine reagent (50 mmol/l NaOCl, 400 mmol/l tau- rine, pH 8.7)
Preincubation of 3 min at 37 °C
25 l t-PA reagent (8 ug/ml in 106 mmol/l arginine, 75 mmol/l NaN3 .0.1% Triton X 100)
Incubation of 5 min at 37 °C
25 of Plasmin-substrate reagent (3 mmol/l HD-Val-Leu- Lys-pNAin 1.5 mol/1 KC1)
Determination of increase in absorbance at 405 nm / min.
The SFP concentration of a patient plasma is calculated by comparison with Standard plasmas (containing 100% and 260% of plasma SFP (in% of normal plasma)), using the for- mula:
= 100 + 160 (Abs. patient sample - Abs. 100%) / (Abs.
260% - Abs. 100%).
The normal ränge of plasma SFP is 50 - 150%. The intra-' assay and inter-assay coefficients of variations were less than 5%. Of n= 645 patient samples submitted for routine analysis in our laboratory, 23 (3.6%) showed elevated con- centrations of SFP. The clinical diagnosis was for n= 5 pa- tients: sepsis, n= 4 : liver cirrhosis with DIC, n= 3: myocar- dial infarction, n=3: pulmonary embolism, n=2: metastazing cancer (with chronic DIC), n=2: apoplex, n=l: subclavian thrombosis in APC resistance, n= 1: terminal renal insuffi- ciency, n= 1: postsurgical ileus. SFP correlated with a) plas- ma fibrinogen, b) C-Yeactive protein, c) thrombocytes, d) leukocytes, e) aPTT, f) PT with correlation coefficients of a) 0.71, b) 0.63, c) 0.51, d) 0.35, e) 0.27, f) 0.03.
Conclusion: Within minutes, hemostasis activation can be monitored using the present specific functional assay for plasmatic soluble fibrin polymers.
A-2
Referenzkurven für die induzierten Thrombozytenaggregationen Th. Eller*, D. Paar*
* Abteilung für Klinische Chemie und Laboratoriumsdiagnostik (Komm. Dir.: Prof. Dr. K. Mann), Zentrum für Innere Medizin, Universitätsklinikum Essen
Fragestellung
Insbesondere in der Diagnostik von angeborenen und erwor- benen Thrombozytopathien sind exakte Untersuchungen der Thrombozytenfunktion von großer Bedeutung. Um eine bes- sere Standardisierung der induzierten Thrombozyten- aggregationen zu ermöglichen, wurden für verschiedene In- duktoren Referenzkurven erstellt.
Material und Methoden
Bei 45 Blutspendern wurden die Aggregations-Zeit-Kurven am APACT-Aggregometer der Fa. LABOR im plättchenrei- chem Plasma für die Induktoren Adrenalin, Kollagen, ADP und Ristocetin registriert und der Aggregationsgrad zu 10 verschiedenen Zeitpunkten (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 90, 120, 180, 300 sec.) ermittelt. Die Meßwerte wurden mittels des Computerprogrammes SPSS statistisch auswertet und an Hand der Richtlinien der IFCC (1) auf das Vorliegen einer Normal Verteilung geprüft.
Ergebnisse
Die Aggregationswerte waren für jeden Induktor normalver- teilt. Auch für die spezifischen Parameter der Aggregation (maximale Aggregation, Aggregationsgeschwindigkeit und Lagphase) wurde eine Normverteilung gefunden. Aufgrund dieser Ergebnisse konnten zur Erstellung der Refe- renzkurven jeweils die ±2s-Werte des Aggregationsgrades eines Meßzeitpunktes eingesetzt werden. Aus diesen Punk- ten wurde eine obere bzw. eine untere Referenzkurve konstruiert.
Schlußfolgerung
Die Anwendung der Referenzkurven in der Diagnostik der Thrombozytenfunktion verbessert die Trennschärfe in Grenzwertbereichen und erleichert die Beurteilung bei ange- borenen und erworbenen Thrombozytopathien.
Literatur
1. Solberg HE. Approved recommendation on the theory of refe- rence values part 5. Statstical treatment of collected reference va- lues. Determination of reference limits. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1987;25:645-56.
A-3
Increased binding of platelets by peripheral blood lymphocytes in myocardial infarction and in acute pancreatitis *
Hans-Äke Fabricius*. Wolfgang Becker*, Stephan Som- mer*, Renate Käferstein*
* Krankenhaus Am Urban> Berlin
Background: Lymphocyte activation and proliferation result from complex cascades of .stimulatory events in which platelet derived growth factors, probably PDGF, have been demonstrated to be essential [1]. As plasma is free of PDGF [2], the question arises, by which mechanism peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) in vivo are enabled to take up platelet-derived substances in sufficient amounts upon acti- vation. PBL have in vitro been demonstrated to develop platelet receptors upon Stimulation [1]. Activation of the cel- lular immune System occurs in myocardial infarction and in acute pancreatitis. In search for a marker for activation of the cellular immune System we investigated the ability of PBL from patients with acute myocardial infarction or acute pancreatitis to bind platelets.
Methods: Platelets were collected from pooled EDTA- blood. PBL were co-incubated with a platelet Suspension at 20 C°. Preparates were stained by Standard panoptical pro- cedures. At least 100 cells were scored.
Resitlts: In the reference collective, the score of platelet binding lymphocytes was 14,6%. In patients with myocar- dial infarction, an average score of 31,1% and in acute pan- creatitis an average score of 30,5% was seen. The differ- ences were highly significant (p<0.000001).
Discussion: The mechanism for regulation of growth of PBL could also in vivo be associated with the expression of cellular platelet receptors.
References
1. Schneider M. Induktion von Thrombozytenrezeptoren in stimu- lierten Blutlymphozyten in vitro. Inaugural-Dissertation, Freie Uni- versität Berlin, 1998.
2. Bowen-Pope DF,Malpass TW, Fester DM, ROSS R. Platelet-de- rived growth factor in vivo: levels, activity, and rate of clearance.
Blood 1984;64:458-69.
A-4
The prothrombin Gene G
2o2io-*A transition is a strong risk factor for pulmonary embo- lism
H. Patscheke*, A. Ruf*, F. Litfin*, S. Kren*, K.H. Reuner* .
* Institute for Medical Laboratory Diagnostics, Klinikum .Karlsruhe Background: It has been reported recently that the mutation 620210 -> A in the 3'-untranslated region of the prothrombin gene i s associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and venous thrombosis. Since in the majority of cases pul-
monary embolism occurs äs a consequence of venous throm- bosis, we addressed the question, if this complicated form of venous thrombosis is also associated with this mutation.
Methods: We analyzed the blood samples of 27 unselect- ed patients (12 male and 15 female; 14 to 78 years old, mean age 53 years) with pulmonary embolism for the presence of the mutation. Blood samples from 245 healthy blood donors (age 20 to 67 years, mean age 45 years) were analyzed äs controls. Pulmonary embolism was verified by Standard pro- cedures. The G —> A Substitution at nucleotide position 20210 was detected by PCR and allele specific restriction digestion.
Resulis: Among the 27 case patients, four subjects (14.8%) were heterozygous for the 620210 -» A mutation in the prothrombin gene, one patient (3.7%) was homozygous, whereas 22 subjects (81.5%) did not carry the mutation.
Among the 245 control persons, 239 subjects (97.6%) did not carry the 620210 -> A mutation, whereas six persons (2.4%) were heterozygous and none was homozygous for the mutation. The difference of frequencies of the.mutation between the group of case patients (18.5%) and controls (2.4%) was statistically significant (p < 0.005, Fisher's exact lest). The mutation 620210 —> A in the prothrombin gene in- creased the relative risk for pulmonary embolism approxi- mately nine-fold (Odds ratio 9.1; 95% confidence interval 2.55 to 32.02) compared to controls. The patient homozy- gous for the 620210 —> A mutation was also heterozygous for.
factor V Leiden mutation. Family examination of this case patient revealed five relatives with the prothrombin gene mutation. All relatives homo-zygous for the mutation had suffered from multiple venous thrombosis.
Conclusion: The 620210 —> A transition in the 3'-untrans- lated region of the prothrombin gene is a strong risk factor for pulmonary embolism.
A-5
The prothrombin Gene G
2o2io->A transition is a risk factor for cerebral venous thrombo- sis but not for ischemic stroke
K.H. Reuner*, H. Rickmann**, A. Ruf*, A. Grau***, E.
Stolz****, E. Jüttler***, K.-F. Druschky**, H. Patscheke*
* Institute for Medical Laboratory Diagnostics,
** Department of Neurology, Klinikum Karlsruhe
*** Department of Neurology, University of Heidelberg
**** Department of Neurology, University of Gießen
Background: It has been recently reported that a G —» A transition at nucleotide position 20210 in the 3x-untranslated region of the prothrombin gene is associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and thus represents a risk factor for deep venous thrombosis and possibly also for peripheral arterial disease. It was the aim of our study to investigate whether this polymorphism also represents a risk factor for cerebral venous and arterial thromboembolism.
Methods: Venous blood samples were collected from 45 patients with cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) and from 131 patients with acute ischaemic stroke orTIA. The control group consisted of 354 healthy blood donors. Genomic J Lab Med 1998; 22 (11): 637-684 641
DNA was isolatcd from peripheral blood Icukocytcs. Ampli- fication of DNA was pcrformcd by PCR. The G -»A transi- tion at nucleotide position 20210 of (he prothromhin gcne was dclccted by allcle spccific reslriction digcstion.
Results: Thc 020210 -* A transition in thc prothrombin gene was found in a hcierozygous form in four out of 45 pa- licnts with CVT (8,9%) and in eight out of 354 healthy con- trol subjects (2.3%). This diffcrcncc was statistically signif- icant (p = 0.010). The G2o2io -» A transition increased the relative risk for CVT approximately five-fold (age-adjusted odds ralio 5,7; 95% eonfidence interval 1.5 to 21.5). In con- trast, in thc group of patients with acute cerebral ischaemia only thrce out of 131 subjects (2.3%) were heterozygous for the 620210 -» A transition, which corresponded to the preva- lencc in the group of healthy blood donors.
Conclitsions: The 620210 -> A transition in the 3'-un- translated region of the prothrombin gene is an inherited risk factor for CVT but obviously not for acute ischaemic stroke or TIA.
A-6
The prothrombin gene G
2o2io->A transition is frequently associated with factor V leiden in patients with venous thromboembolism and leads to thrombosis in 100% of cases when associated with two other risk factors for thrombophilia
A. Ruf*, H. Patscheke*, F. Litfin*, S. Kreft*, K.H. Reuner*
* Institute for Medical Laboratory Diagnostics, Klinikum Karlsruhe Background: Thrombophilia has been demonstrated to be a complex disorder often caused by the coincidence of inher- ited and/or environmental risk factors. Recently, it has been reported that a 620210 —> A transition in the 3'-untranslated region of the prothrombin gene is associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and venous thrombosis. It was the aim of this study to investigate whether the 620210 -» A transition in the prothrombin gene is a common additional thrombotic risk factor in thrombophilic patients who are car- riers of the factor V Leiden mutation.
Methods: We analyzed the blood samples from 1256 con- secutive patients with suspected thrombophilia for the pres- ence of the factor V Leiden mutation by allele specific PCR.
Subsequently, we analyzed the samples of 127 patients which were detected äs carriers of factor V Leiden for the presence of the 620210 -> A transition in the prothrombin gene. Blood samples from 354 healthy blood donors were analyzed äs controls. Moreover, we examined the members of a family with both mutations for thromboembolic events and additional risk factors.
Results: Among the 354 control subjects, 346 (97.7%) did not carry the 620210 —* A transition in the prothrombin gene, whereas 8 persons (2.3%) were heterozygous and none was homozygous for the mutation. In the group of 127 patients with suspected thrombophilia who are carriers of the factor V Leiden mutation, 8 subjects (6.7%) were heterozygous ör homozygous carriers of the 620210 -» A mutation. This dif- ference was statistically significant (p=0.04; Fisher's exact
test). In a second step we restricled our investigation to the subgroup of carriers of the factor V Leiden mutation with verified venous thrombosis (n = 51). Within this population, 7 out of 51 patients (13.7%) were carriers of the prothrom- bin gene mutation (p=0.001). On the other band, in a sub- group of carriers of thc factor V Leiden mutation with veri- fied artcrial disease (e.g. myocardial infarction or stroke), only l out of 15 patients (6.7%) carried the 620210 -» A mu- tation, which was not statistically significant (p=0.32).
When invesligating 12 patients (including the members of one family with thrombophilia) who carry both mutations, it could be observed that only one of 4 persons (25%) who are heterozygous carriers of both mutations ("double hint") had suffered from a deep venous thrombosis. However, in the group of 8 patients who were homozygous for one and het- erozygous for the other mutation or were heterozygous for either mutation with an additional risk factor, e.g. protein S deficiency ("triple hint"), all subjects (100%) had suffered from thromboembolism till the age of 62 years.
Conclusions: The 620210 —> A transition in the prothrom- bin gene is frequently associated with factor V Leiden in pa- tients with venous thromboembolism and leads to thrombo- sis in 100% of cases when associated with two other risk factors for thrombophilia ("triple hint").
A-7
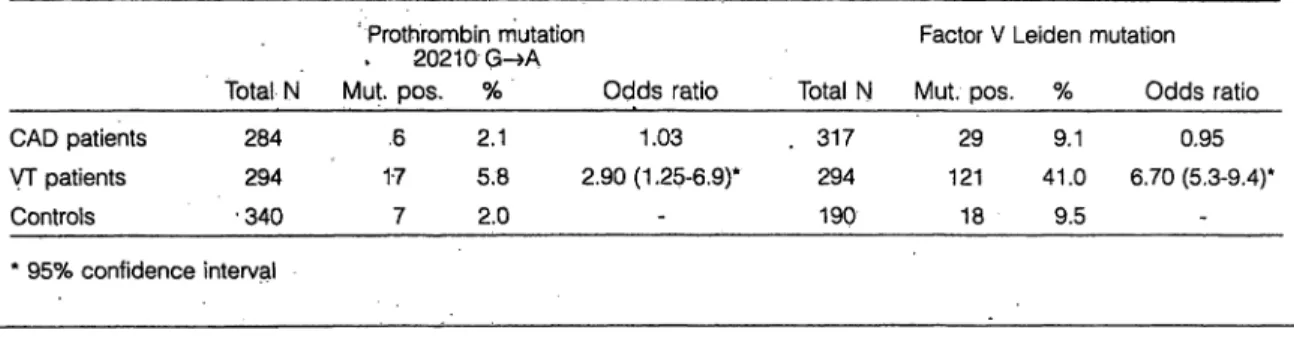
The Prevalence of the Prothrombin 20210 G->A Mutation in Angiographically Confirmed Coronary Artery Disease W. Prohaska*. M. Schmidt*, H. Mannebach**, U. Gleichmann**, K. Kleesiek*
* Institut für Laboratoriums- und Transfusionsmedizin
** Kardiologische Klinik, Herz- und Diabeteszentrum NRW, Uni- versitätsklinik der Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen We screened DNA samples from 284 patients with coronary artery disease for the presence of the mutation 20210 G-»A of the prothrombin gene using PCR followed by restriction enzyme digestion and analysis äs originally described by Poort et al. [1]. It has been reported that this mutation con- fers a significant risk increase for venous thrombosis. Our aim was to investigate whether the occurrence of this new mutation is more frequent in patients with coronary artery disease defmitely diagnosed by coronary angiography than in a control group of healthy persons and patients with ve- nous thrombosis. Furthermore we were able to compare the results with pre-existing, data of factor V Leiden analysis in the same groups.
Among 340 healthy controls we found 7 persons (2.0%) carrying the prothrombin 20210 G—»A mutation. 6 out of 284 patients with coronary artery disease (2.1%) carried the mutation (odds ratio: 1.03), whereas 17 out of 294 patients with venous thrombosis (5.8%) were positive for this muta- tion (odds ratio: 2.90; 95% eonfidence interval: 1.25 - 6.9).
The data for the factor V Leiden mutation also revealed no increased association with CAD (odds ratio: 0.95) but con- firmed the known risk for venous thrombosis (odds ratio:
6.70;'5.3-9.4).
Table 1 Prevalence of the prothrombin mutation 20210 G-»A and the factor V Leiden mutation in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), patients with venous thrombosis (VT) and healthy controls
CAD patients VT patients Controls
* 95% confidence Total N
284 294
•340 interval
'Prothrombin mutation
* 20210G-»A
Mut pos. % Odds ratio .6
17 7
2.1 1.03 5.8 2.90(1.25-6,9)*
2.0
Factor V Total N Mut. pos . 317 29
294 121 190 18
Leiden mutation
% Odds ratio 9.1 0.95 41.0 6.70(5.3-9.4)*
9.5
124 out of 288 patients negative for the factor V Leiden mutation and 10 out of 29 patients positive for this mutation had a history of at least one myocardial infarction (odds ratio: 0.7; 0.3 - 1.5). 120 out of 278 CAD patients without the prothrombin gene mutation and 2 out of 6 patients car- rying the mutation had a myocardial infarction (odds ratio:
0.66; 0.12 - 3.6). According to these data the hypothesis that the prothrombin 20210 Gr-»A Variation is a risk factor for common coronary artery disease or the occurrence of my- ocardial infarction is not supported (tab. 1).
Reference
1. Poort S R, Rosendaal FR, Rcitsma PH, Bertina RM. A common genetic Variation in the 3'-untranslated region of the prothrombin s;ene is associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and an Tncrease in venous thrombosis. Blood 1996;88:3698-703.
A-8
First Identification of a Mutation in theTFPI Gene
M. Schmidt*, T. Brinkmanrf, C. Götting*, W. Prohaska*, K. Kleesiek*
* Institut für Transfusions- und. Laboratoriumsmedizin, Herz- und Diabeteszentrum Nordrhein Westfalen, Universitätsklinik der Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen
Within the last decade tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) has been described äs an impoftant regulator in the extrinsic blood coagulation pathway [1]. Although the regulatory bio- chemical role of TFPI is evident, there is still a gap con- cerning the clinical significance'of this proteinase inhibitor.
The definition of a clinical TFPI deficiency seems to be a more complex problem compared with other blood coagula- tion inhibitors like antithrombin III and protein C. The ac- tivity and concentration of circulating TFPI may not be con- sidered äs a true measure of in vivo levels, and its determi- nation in plasma samples by immunological methods or functional assays, which are based on the ability of TFPI to inhibit FVIIa/TF complexes in the presence of FXa, has been shown to be insufficient to detect a clinical deficiency.
Therefore, we have screened genomic DNA samples of blood donors and thrombotic patients for alterations in the TFPI gene to assess the contribution of a modified TFPI to venous thromboembolic diseases. We have detected a single nucleotide Substitution (C-»T) in exon 7 leading to a prolin to leucin exchange at amino acid position 151 of the protein [2]. The prevalence of heterozygous carriers in German un- related blood donors (n=2480) is 0.16%.
Three unrelated persons out of 15 probands from 6 fami- lies carrying the genetic mutation suffered from venous thrombosis. However, due to the small number the carrier- ship of the trait just failed to show a statistically significant risk for venous thrombosis compared with blood donors without the TFPI mutation (odds ratio: 3.7; 95% confidence interval: 0.83-16.6). To clarify this question it is necessary to identify more subjects carrying the inherited abnormality.
References
1. Broze GJ Jr. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Haemostaseologie 1997;17:73-7.
2. Kleesiek K, Schmidt M, Götting C, Brinkmann T, Prohaska W.
A First Mutation in the Human Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Gene Encoding [P151L]TFPI. Blood (in press)
A-9
Assoziation von Cytomegalievirusinfektion und venöser Thromboembolie
C.M. Schambeck*, K. Hinney*, J. Gleixner*, F. Keller"
* Zentrallabor und Gerinnungsambulanz der Medizinischen Uni- versitätsklinik Würzburg
Fragestellung: Das Cytomegalievirus (CMV) selbst löst zum einen eine Hyperkoagulabilität aus. Zum anderen ver- mögen Infektionen der Leber und Affektionen des Endothels eine erhöhte Faktor VIII-Aktivität zu bewirken. Erhöhte Faktor Vlll-Spiegel wurden 1995 als thrombophiles Risiko beschrieben. Das latente und reaktivierbare Virus mit hohem Durchseuchungsgrad mag hier eine ursächliche Rolle spie- len.Material und Methoden: Es wurden aus 557 Patienten mit der Vorgeschichte einer venösen Thromboembolie 34
J Lab Med 1998; 22 (11): 637-684 643
Patienten mit einem erhöhten Faktor VIIIf wobei bekannte Ursachen für eine Faktor VlII-Erhöhung ausgeschlossen wurden, und 34 allers- und geschlechlsentsprechende Pati- enten mit normwcrtigcm Faktor VIII ausgewählt, ferner 34 altcrs- und gcschlcchts-entsprcchendc Blutspender als Kon- trollen herangezogen. Die Faktor VHI-Aktivitüt wurde mit einem chmmogencn Assay der Fa. Dade-Behring (Marburg, Deutschland) am Elcctra 1000 C, CMV-IgG und -IgM am IMx (Abbott, Chicago) gemessen.
Ergebnisse: Eine akute Infektion war nur bei einer Thrombosc-patientin mit erhöhtem Faktor VIII nachzuwei- sen. Die CMV-IgC-Titcr der drei Kollektive unterschieden sich nicht signifikant voneinander. Wurden jedoch Fälle mit hohem IgG-Titer (> 300 AE/ml) zusammengefasst, übertraf hierbei die Anzahl der Thrombosepatienten die der Bluts- pender signifikant (p<0,01 bzw. p=0,03). Dabei machte es keinen Unterschied, ob Thrombosepatienten eine erhöhte Faktor VTII-Aktivität aufwiesen oder nicht.
Schlußfolgerung: Eine CMV-Infektion könnte mit einem venösen Thromboserisiko assoziiert sein, wobei ein ursäch- licher Zusammenhang erst noch zu belegen wäre. Ein Zu- sammenhang mit der Faktor VIII-Aktivität scheint eher un- wahrscheinlich.
A-10
Analysis of Antigen Specificity and Functional Activity of two Human Mono- clonal IgG Antiphospholipid Antibodies K.J. Lackner*, C. v. Landenberg*, R,v. Landenberg**, G. Schmitz*
* Institute for Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine
** Dept. of Internal Medicine l, University of Regensburg To characterize the binding specificity and pathophysiologic relevance of antiphospholipid antibodies (APA), B-cells from patients with positive APA tests were immortalized and screened for production of specific IgG. Two human mono- clonal IgG-APA, HL-5B and RR-7F were generated from a patient with primary antiphospholipid syndrorae and recur- rent cerebral microemboli (H.L.) and from a SLE-patient without evidence of thrombosis (R.R.). While both have similar binding specificities, HL-5B has an apparently ten- fold higher affmity towards cardiolipin and phosphatidylser- ine than RR-7F. Analysis of the transcribed VH-genes showed that HL-5B is highly mutated indicating affmity maturation, while RR-7F has a germline configuration. To analyze the prothrombotic potential, their effect on procoag- ulant activity (PCA) of human monocytes and bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAEC) was determined. Cells were incu- bated for 6 hrs with the respective mAPA or patient plasma, or LPS äs positive control. PCA was determined by a single stage clotting assay and expressed äs the ratio of the coagu- lation times observed with cells preincubated with media only divided by that observed after incubation with the ago- nist. Induction of PCA is reflected by a PCA-ratio >1. The PCA-ratio induced by serum from H.L. was 1.8 compared to 1.4 with serum from R.R. At l g/ml HL-5B yielded a PCA- ratio of l .6 ± 0.2 while RR-7F induced an insignificant rise to 1.1 ± 0.2. Dose response curves showed that on a molar
basis HL-5B is approx. 50-fold more potent than RR-7F in PCA-induction. Neither antibody induced PCA in BAEC. In summary, our data indicate that minor differences in binding specificity and affinity of APA may cause significantly dis- cordant cellular effects, which may be related to the clinical conr.se of the affectcd patients. These differences cannot be predicted by the currently used ELISAs.
B-1
Die Bedeutung immunologischer Nachweis- verfahren für die Grenzwertfestsetzung pro- phylaktischer Thrombozytentransfusionen bei Patienten mit Leukämie
W. Springer*, R. Dickerhoff**, A. von Rücker*
* Institut für Klinische Biochemie, Universität Bonn
** Johanniter Kinderklinik, St. Augustin
Die empfohlene Schwelle für eine prophylaktische Throm- bozytentransfusion bei Patienten mit Leukämie schwankt in der Literatur zwischen 5000 und 20000 Thrombozyten/ . Diese Abweichungen sind darauf zurückzuführen, daß kon- ventionelle Blutanalyseautomaten nur Partikel mit einer de- finierten Größe und keine Thrombozyten erkennen können.
Deshalb werden u.a. hämostaseologisch aktive Mikroparti- kel thrombozytärer Herkunft unterhalb der Meßgrenze von 2 fl nicht erkannt.
Bei 14 Patienten mit akuter myeloischer Leukämie wur- den unter Therapie Thrombozyten und Mikropartikel mittels Durchflußzytometrie (anti-CD61 und anti-CD42b) be- stimmt. Bei den Patienten lag die Anzahl der Mikropartikel zwischen 0 bis 76% der jeweiligen Thrombozytenzahl.
Keine Blutungen traten bei Patienten mit Thrombozytenzah- len > 5000/ auf. Die Mikropartikelanzahl lag gewöhnlich über 3000/ . Blutungen traten nur bei 4 Patienten auf, deren Thrombozytenzahl einschließlich der Mikropartikel (Anteil < 2%) zwischen 2300-4900 pro lag.
Unsere Untersuchungen zeigen, daß die prophylaktische Thrombozytentransfusionsgrenze bei Patienten mit Leukä- mie bei 5000 Thrombozyten/ liegt. Zur klinischen Ein- schätzung ist es allerdings unabdingbar, daß die Anzahl der Mikropartikel bekannt ist. Diese Beobachtung unterstreicht die Notwendigkeit,; immunologische Detektionsverfahren in hämatologische Routinelaboratorien einzuführen, wobei ein Durchflußzytometer oder ein neuerer mit entsprechenden Methoden ausgerüsteter Blutanalyse-automat zur Verfügung stehen sollte. Dadurch könnten Thrombozytentransfusionen reduziert und Kosten eingespart werden.
B-2
Functiona! lymphocyte subsets are differing in surface sialylation pattern
H. J. Groß*, A. Schmid-Kotsas*, M.G. Bachern*, R. Schwartz-Albiez**, A. Grünert*
* Dep. Clinical Chemistry, University of Ulm
** Dep. Tumorimmunology, DKFZ' Heidelberg
Surface exposed sialoglycans are important structures for cellular interactions. Certain a2,3- or a2,6-sialylated gly- cans represent ligands for adhesion proteins (selectins, CD22, sialoadhesin). Sialylation of galactose sites blocks binding of galactose-dependent galectins. Therefore, the specific sialoglycan pattern at the cell surface is supposed to be decisive for cell function. Human lymphocytes were in- vestigated for sialylation, sialyltransferase- and galectin ex- pression.
Methods: Expression of surface exposed galactose and sialylation pattern (a2,3-/ct2,6-linkage) was determined by flow cytometry after specific enzymatic labelling and was correlated to the functional lymphocyte subset defined by CD-antibody staining. Expression of a2,6-sialyltransferase, of galectin l and -3 was investigated by RT-PCR.
Results: The highest overall sialylation of exposed galac- tose sites was observed with human B-cells (45-65%), the lowest with CD8+ T-cells (30-40%). A higher level of sur- face galactose on T cells correlated to a high expression of CDlla and CD26. Resting T-cells (CD45RA+) were sialy- lated in a2,6-linkage to about 90%, high expression of CDlla correlated to a 3-4fold enhanced sialylation in a2,3- linkage. NK-cells were sialylated by 90%. in a2,3-linkage, B-cells by 85% in a2,6-linkage.
Expression of a2,6-sialyltransferase, galectin 3 and -l was high in all functional subsets investigated. In case of B- and T-ceDs high mRNA level of a2,6-sialyltransferase was in accordance to the surface sialylation pattern, in case of NK- cells in opposite to the low a2,6-sialylation.
Conclusion: The data prove significant differences in cell surface sialylation for functional lymphocyte subsets. The pattern is not simply determined by respective sialyltrans- ferase expression. Expression of galectin adhesion proteins is not correlated to the level· of surface galactose sites.
B-3
Detection of leukocytes harboring cytomegalovirus by In-cell-PCR and flow cytometry
D. Laßner*, S. Bosse*, H. Remke*, M. Ladusch**, B.
Pustowoit***., U.G. Liebert***., M. Wenzke****, R. Schwarz****, K. Kohlhaw****, J. Hauss**** and O. Wagner*
* Department of Clinical Chemistry and Pathobiochemistry,
** Department of Zoology,
*** Department of Virology,
**** Department of Abdominal, Transplantation and Vascular Sur- gery, University of Leipzig
Ahm Infection with human cytomegalovirus (CMV) is asso- ciated with allograft rejection and morbidity in immuncom- promised transplant recipients. The underlying pathomech- anisms of CMV-associated rejection and the ways of trans- mission of virus by leukocytes in peripheral blood have not been fully elucidated.
The determination of virus load is of importantance for monitoring the optimal treatment of viral infection. PCR technology following reverse transcription of mRNA pro- vides an extremly sensitive tool for detection of low levels of gene expression. Usually the virus load is determined by quantitative measurement of viral genomes or transcripts by PCR in a defmite amount of DNA or RNA from a whole leukocyte population. However, no correlation of copy num- bers and the percentage of cells expressing this gene can be achieved by this methodology. Therefore in situ amplifica- tion was established äs a new method for detection of intra- cellular nucleic acids from indiyidual cells [1].
In-cell-PCR is the combination of in situ PCR and subse- quent analysis Of cells by flow cytometry. This method is used to detect cells with gene expression in a large popula- tion. Aim of this study was to establish· an in-cell-PCR for detection of leukocytes harboring cytomegalovirus. This technique may be useful for monitoring CMV infection of white blood cells in correlation with cünical Symptoms of tfansplantation patients.
Material and Meihods: The in-cell-PCR method com- bines the intracellular amplification of mRNA by RT-PCR in fixed cells with FITC labeled primers and flow cytometric analysis of cells [2, 3]. A defmite amount of fixed cells was incorporated in a reaction vessel. The intracellular CMV- mRNA was transcribed specifically into cDNA by AM V re- verse transcriptase and the newly generated cDNA was am- plified by PCR with Taq DNA polymerase using orie fluo- rescent primer. Cells were analyzed on FACSCalibur (Bec- ton Dickinson) flow cytometer. Fluorescent DNA inside cells could be observed by conventional fluorescence mi- croscopy after dotting the cells on a slide. The number of CMV-infected cells was monitored by In-cell-PCR and com- pared to results of usual nested RT-PCR.
Results and Conclusions: We have developed a method for intracellular transcription and amplification of viral RNA and DNA. This assay allows the detection of CMV infection and the delermination of the percentage of infected cells.
Leukocytes of patients with viremia or antigenemia for CMV were analysed by In-cell-PCR. Intracellular amplifica- tion of viral DNA or RNA allowed the discrimination of
temporale virus or viremia insidc cells. Furlhcr studies are ncccssary for cvaluation of thc predictivc value of virusload in leukocytes of transplant rccipienls on clinical complica- tions likc allograft-direcled inflammation and rcjection of transplanted organ.
References
1. Nuovo et al. Am J Pathol 1991; 139:847-54.
2. Haa.sc et al. Proc Natl Acad Sei USA 1990:87:4971-5.
3. Emblcton et al. Nucl Acids Res I992;20, 3831-7.
B-4
Heparan sulfate proteoglycan expression is induced during early erythroid
differentiation of multipotent haematopoietic stem cells
G. Stöcker*, Z. Drzeniek*, B. Siebertz*, U. Just**, W. Ostertag***, and H.-D. Haubeck*
* Institut für Klinische Chemie und Pathobiochemie, Universitäts- klinikum der RWTH Aachen
** Institut für Klinische Molekularbiologie - GSF Forschungs- zentrum München
*** Heinrich-Pette-lnstitut für Experimentelle Virologie und Immunologie Hamburg
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans of bone marrow stromal cells and their extracellular matrix are important components of the microenvironment of haematopoietic tissues and are in- volved in the interaction of haematopoietic stem and stromal cells. Whereas previous studies have emphasized the role of heparan sulfate proteoglycan synthesis by bone marrow stro- mal cells, we have recently shown that the human haematopoietic progenitor cell line TF-1 also expressed a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. Immunochemical and Northern blot analysis of this heparan sulfate proteoglycan revealed, that it was not related to the syndecan family of heparan sulfate proteoglycans nor to known members of the glypican gene family. To answer the question, whether the expression of heparan sulfate proteoglycans is associated with the differentiation state of haematopoietic progenitor cells, we have analyzed the proteoglycan synthesis of sever- al murine and human haematopoietic progenitor cell lines.
Proteoglycans were isolated from metabolically labelled cells and purified by several Chromatographie Steps. Isola- tion and characterization of proteoglycans from the cell lines HEL and ELM-D, which like TF-1 cells have an immature erythroid phenotype, revealed that these cells synthesize the same heparan sulfate proteoglycan, previously detected in TF- l cells, äs a major proteoglycan. In contrast, cell lines of the myeloid lineage, like the myeloblastic / promyelocyt- ic cell lines B l and B2, do not express heparan sulfate pro- teoglycans. Taken together, these data strongly suggest that expression of this heparan sulfate proteoglycan in haematopoietic progenitor cell lines is associated with the erythroid lineage. To prove this association we have ana- lyzed the proteoglycan expression in the non-leukemic mul- tipotent stem cell line FDCPMix-A4 after induction of ery- throid or granulocytic differentiation. Our data clearly show,
that heparan sulfate proteoglycan expression is induced dur- ing carly erythroid differentiation of multipotent haematopoietic stem cells. in contrast» during granulocytic differentiation no expression of heparan sulfate proteogly- cans was observed. The function of this heparan sulfate pro- teoglycan during early erythroid differentiation is at present under study.
B-5
Molecular cloning of human K-glypican expressed in kidney and haematopoietic progenitor and stromal cells
B. Siebertz*, G. Stöcker*, Z. Drzeniek*, and H.-D. Haubeck*
* Institut für Klinische Chemie und Pathobiochemie, Universitäts- klinikum der RWTH Aachen
Heparan sulphate proteoglycans of bone marrow stromal cells and their extracellular matrix are important compo- nents of the microenvironment of haematopoietic tissues and are involved in the interaction of haematopoietic stem and stromal cells. Previous studies have emphasized the role of heparan sulphate proteoglycan synthesis by bone marrow stromal cells. In the present study we describe the expres- sion of K-glypican, belonging to the glypican family of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans, in bone marrow stro- mal cells and haematopoietic progenitor cells of human and murine origin. We have cloned the CDNA of the human ho- mologue of K-glypican from one of these cell lines, the haematopoietic progenitor cell line TF- l. Human K-glypi- can has a homology of 91% with murine K-glypican on the nucleic acid level. The deduced protein sequence has a ho- mology of 92% and corresponds to a molecular weight of 57 kDa. To analyze the expression of K-glypican on the protein levei specifie peptides were synthesized and used for the production of polyclonal antibodies in rabbits. Western blot analysis showed expression of K-glypican äs a heparan sul- phate proteoglycan with a molecular weight distribution of >
.200 - 100 kDa and a core protein of 57 kDa in the human haematopoietic progenitor cell line TF- l äs well äs in human kidney. In contrast, these antibodies did not react in the Western blot with the murine ceH lines, indicating that these antibodies are specifie for the human K-glypican. The antibodies were used also for the analysis of the tissue dis- tribution of K-glypican. In human kidney a specifie staining of proximal tubuli in the cortex and a strong staining of col- lecting ducts in the medulla was observed. In contrast, jglomeruli were comple^ely negative. This specifie distribu- tion might be of relevance with respect to the function of K-glypican in kidney. Furthermore, the specifie function of K-glypican in the interaction of haematopoietic stem and bone marrow stromal cells has to be analyzed in detail.
B-6
Reaktionsverhalten von Antiseren der Spezifitäten Anti-S, Anti-s, Anti-Fya, Anti- Fyb, Anti-Jka,und Anti-Jkb bei Verwendung des Gel-Zentrifugationstests
Th. Rogge*, .- . Fabricius*
* Städtisches Krankenhaus Am Urban, Berlin
Fragestellung: Die Bestimmung der Blutgruppenmerkmale S, s und im Duffy- und Kidd-System wird derzeit noch über- wiegend mit coombsreaktiven Antiseren durchgeführt [1].
Neben der Durchführung im Röhrchentest findet der Gel- Zentrifugationstest zunehmend Anwendung [2]. Es wird die Eignung von coombsreaktiven Antiseren verschiedener Her- . steller bei Verwendung der LISS-/Coombskarte des Herstel-
lers DiaMed im Gel-Zentrifugationstest untersucht.
Materialien und Methoden: Untersucht wurden Antiseren folgender Spezifitäten:
Anti-S, Anti-s, Anti-Fya, Anti-Fyb, Anti-Jka und Anti-Jkb von 2 Herstellern.
Titration in geometrischer Verdünnungsreihe gegen Erythrozyten mit homo- und heterozygoter Merkmalsau- sprägung im Gel-Zentifugationstest.
Ergebnisse: Fast alle Antiseren zeigen unverdünnt ein deutliches Prozonen-Phänomen. Bei zunehmender Verdün- nung nimmt die Reaktionsstärke bis zu einem Plateau zu.
Antiseren verschiedener Hersteller zeigen sowohl Unter- schiede in der maximalen Reaktionsstärke (Höhe des Pla- teaus) als auch in der maximalen Titerhöhe (maximale Ver- dünnung, bei der noch ein positives Ergebnis ermittelt wird).
Dosiseffekte werden für die Antigene S, s und Kidd fest- gestellt. Im Duffy-System reagieren Zellen unterschiedlicher Zygotie identisch stark.
Schlußfolgerungen: Die untersuchten coombsreaktiven Antiseren können problemlos zur Antigenbestimmung im Gel-Zentrifugationstest eingesetzt werden. Die Verdünnung des Antiserums ist notwendig und führt zu einer deutlichen Kostensenkung, die die Zusatzausgaben für die DiaMed- Karte übertreffen. Für jedes Antiserum eines Herstellers ist die optimale Verdünnung zu ermitteln. Diese sollte bei jedem Chargenwechsel erneut evaluiert werden.
B-7
Epitope Determination of Coeliac Disease- related Autoantibodies using Phage Display Peptide Library
A.A. Osman*, Th. Günnel*. H. Uhlig*, J. Schneider-Mer- gener**, Th. Mothes*
* Institut für Klinische Chemie und Pathobiochemie der Universität Leipzig
** Institut für Medizinische Immunologie der Humboldt-Universität, Berlin
Coeliac disease (CD) is characterized by disturbed small bowel function connected with diarrhoea, weight loss, and anaemia. Furthermore. there is an increased risk for malig- nancy. Gliadin antibodies (AGA) and autoantibodies (EmA) are serological markers of CD with the latter directed against reticulin-like fibres in Lamina muscularis mucosae.
Diagnosis of CD is carried out histologically by means of biopsy and serologically by estimation of AGA and EmA in serum. Although determination of EmA is only semiquanti- tive it is sensitive and specific for CD. Detection of CD spe- cific epitopes or mimitopes via phage display and their ap- plication in ELISA would improve and simplify diagnosis.
In the present work IgA from 5 CD patients was isolated using anti-human-IgA column. The purity and reactivity of isolated IgA was proved by electrophoresis, western-blot and immune fluorescence. A phage library expressing ran- dom heptapeptides was used to determine EmA epitopes.
The library was incubated with isolated IgA fixed to plastic surface. Specifically bound phage were eluted and amplified in E. coli. After 3 rounds of selection, DNA of phage clones coding for peptide insert was sequenced.
32 consensus sequences (CS) were determined. To check the specificity, peptides with CS were synthesized on cellu- lose membrane via their C-terminus. The reactivity of sera from 25 CD patients and 25 healthy controls was examined in western-blot. Seven peptides were reactive only with CD patients' sera. Currently antibodies against these peptides are raised.
Results show that phage display is a powerful technique for investigation of autoantigenic epitopes.
Literatur
1. Rinas, U. Blutgruppenserologie. 3. Auflage. Berlin (DE): VEB Verlag Volk und Gesundheit, 1988.
2. American As'sociation of Blood Banks: The Antiglobulintest.
In: Technical Manual, 11. Auflage, 1993;196-202.
B-8
Einfluß der Glykosylierung von L-Selektin auf seine biologische Funktion
S. Emig-Vollmer*. B. Volz*, C. Reger*, N. Debus**, W. Semmler**, R. Tauber *
* Universitätsklinikum Benjamin Franklin, FU Berlin
"Institut für Diagnostikforschung, Berlin
Fragestellung: Selektine bilden eine Familie von Zell- adhäsionsmolekülen und haben eine zentrale Bedeutung für den Ablauf der Adhäsionskaskade, die zur Extravasation von Leukozyten führt. Selektine sind für den ersten Schritt die- ser Adhäsionskaskade, dem „Rolling" der Leukozyten ent- J Lab Med 1998; 22 (11): 637-684
lang des Gclaßendothcls verantwortlich. Daher haben die Sclektinc eine wichtige Rolle bei allen Vorgängen, die mit einer verstärkten Infiltration des Gewebes mit Leukozyten cinhcrgehcn (akute bzw. chronische Entzündung, Ischämie- Reperlusionssyndrom z.B. nach Myokardinfarkt oder Apo- plex). Sclektinc sind nionomere Glykoprotcinc und binden die Glykanstrukluren ihrer Bindungspartner. Wir haben un- tersucht, welchen Hinfluß die Glykosylicrung von L-Selek- tin aufsein Bindungsverhalten hat.
Material und Methoden: Hierfür wurde humanes L-Sc- Icktin in verschiedenen Zellinicn (BHK und K562) cekom- binant hergestellt. Die Glykanstrukturen der gereinigten For- men von L-Selektin aus den beiden Zelllinien wurden mit- tels Lektinblot charakterisiert. In einem statischen Bin- dungsassay und einem unter Flußbcdingungen wurde die biologische Aktivität der unterschiedlich glykosylierten For- men von L-Selektin untersucht.
Ergebnisse und Schlußfolgerungen: Für die rekombinan- ten Formen von L-Selektin aus BHK- und K562-Zellen wurde mittels Lektinblot eine unterschiedliche Glykosylie- rung nachgewiesen. Terminale Sialinsäuren in a2,6 Position wurden ausschließlich auf L-Selektin aus K562-Zellen ge- funden. L-Selektin aus BHK Zellen weist dagegen nur ter- minale Sialinsäuren in a2,3-Position auf. Zusätzlich war das L-Selekin aus BHK Zellen viel ausgeprägter sialyliert als das aus K562-Zellen. Sowohl im statischen Bindungsassay als auch unter Flußbedingungen zeigte L-Selektin aus K562- Zellen im Vergleich zu L-Selektin aus BHK-Zellen eine höhere Bindungsfähigkeit an alle untersuchten Testzellen.
B-9
A Particle-Enhanced Reagent for the Immunonephelometric Determination of soluble Transferrin Receptor
D. Kraul*, H. Althaus*, G. Walter*, H.-R Harthus*, L. Quinzio*
* Dade Behring Marburg GmbH, Marburg, Germany
N Latex sTfR i s a particle-enhanced assay for immunoneph- elometric determination of soluble transferrin receptor (sTfR) in human serum or heparin plasma by the Behring Nephelometer Systems (BN II, BNA, BN 100) of Dade Behring. The concentration of soluble (circulating) transfer- rin receptor is proportional to cell-bound tränsferrin receptor and therefore reflects iron requirement of the cells together with erythropoietic activity of the body. In combination with ferritin', sTfR promotes an efficient evaluation of iron me- tabolism disorders. In the presence of sTfR, latex particles coated with monoclonal antibpdies against sTfR are aggluti- nated in a dose-dependent manner and the resulting increäse' in light scattering is determined over 6/12 minutes in a fixed time mode. The new assay showed very good precision at all concentration levels, coefficients of Variation (CV) accord- ing to analysis of variance (n = 40) for the basic measuring ränge of 0.136 to 4.36 mg sTfR/L sTfR: intra assay CV of 1.39 to 2.95%, inter assay CV of 0.79 to 2.06%, and total CV of 1.46 to 3.32%. Potentially interfering substances, such äs rheumatoid factors and HAMA did not affect results.
Good agreement of results was obtained in comparison to a
commcrcially available sTfR ELISA, coefficient of correla- tion of r = 0.976 (n= 46). N Latex sTfR combines high ana- lyticul quality with ease of usc on an automated analyzer.
B-10
Ultrasensitive CRP-Bestimmung mit einem neuen turbidimetrischen Latexreagenz auf Basis monoklonaler Antikörper
B. Schmidt*, H.-R Harthus*, G. Walter*, M. Lammers*
- Dade Behring Marburg GmbH, Marburg, Germany
C-reaktives Protein (CRP) ist das klassische Akute-Phase- Protein, dessen Serumkonzentration im Verlauf einer gene- rellen, unspezifischen Antwort auf infektiöse und nichtin- fektiöse Entzündungsprozesse ansteigt.
Ein neues Indikationsgebiet für die CRP-Bestimmung er- schließt sich mit der Rolle von CRP als kardiovaskulärer Ri- siko-Parameter.
Ziel der Arbeit war es, hierfür ein neues partikelverstärk- tes Reagenz auf Basis monoklonaler Antikörper für die im- munturbidimetrische Bestimmung zu entwickeln. Monoklo- nale Antikörper mit hoher Agglutinationsfähigkeit und der Spezifität für ein auf nativem CRP vorhandenem Epitop wurden selektiert.
Als Meßsystem wird das TurbiTimeSystem verwendet, das eine quantitative Erfassung der Immunpräzipitation in sehr kurzen Zeiten erlaubt.
Durch unterschiedliche Probenverdünnung kann mit dem neuen Turbiquant CRP mono (ultrasensitiv) in zwei Meßbe- reichen bestimmt werden. So reicht der Meßbereich mit 50
1:21 verdünnter Probe von 2,5 bis 600 mg/1 und mit 50 unverdünnter Probe von 0,5 bis 20 mg/1. Das neue Reagenz weist insgesamt eine gute Linearität und eine ausgezeichne- te Chargenkonstanz auf und zeigt keine Interferenzen mit bekannten Störfaktoren.
Die Präzision ermittelt nach dem Varianzmodell ergibt Gesamtvariationskoeffizienten zwischen 3,5 und 7,8%. Im Vergleich mit dem immunnephelometrischen N Latex CRP mono Assay von Dade Behring ergibt sich sowohl für den normalen als auch den ultrasensitiven Meßbereich eine gute Übereinstimmung:
- normaler Meßbereich (n = 48):
y (Turbiquant CRP mono) = 1.02 (N Latex CRP mono) - 1.43 mg/1, r = 0.983
- ultrasensitiver Meßbereich (n = 45):
y (Turbiquant CRP mono) = 1.04 (N Latex CRP mono) + 0.10mg/l, r = 0.9,79
Damit steht für das TurbiTimeSystem ein verbessertes CRP- Reagenz zur Verfügung, das auch im ultrasensitiven Meßbe- reich verläßliche Resultate liefert.
C-1
Nachweis unterschiedlicher
Knochenresorptionsparameter im Urin C. Zingler*. S. Kleist*, S. Mansch**, R. Hampel***, R Schuft-Werner*
- Institut für Klinische Chemie und Pathobiochemie der Universität Rostock
** Universitätsfrauenklinik der Universität Rostock
*** Klinik für Innere Medizin der Universität Rostock
Deoxypyndinolin-Crosslinks (DPD), aminoterminale N- Telopeptide (NTx) und carboxyterminale C-Telopeptide (CTx) sind Bestandteile der Quervernetzung von Typ l Kol- lagen in der organischen Knochenmatrix. Erhöhte renale Ausscheidungen dieser Marker gelten als Indikatoren einer gesteigerten Osteoklastenaktivität (1). Für die Bestimmun- gen dieser Degradationsprodukte im Urin werden sowohl Sammelurine (NTx) als auch 2. Morgenurine (CTx) bzw.
beide (DPD) empfohlen.
Zielstellung:
- Untersuchungen zur intraindividuellen Abhängigkeit der Ausscheidungskonzentrationen von NTx, DPD (freie) und CTx sowie Vergleich von knochengesunden Kon- troll- und Karzinompatientinnen
- Gegenüberstellung der Meßergebnisse aus Sammelurin und 2. Morgenurin
Material und Methoden:
Bei 38 knochengesunden Frauen (Alter 36-58 Jahre) wurden im Urin freies DPD, NTx und CTx in der zweiten Zyklus- hälfte während 5 Zyklen bestimmt. Die Messungen erfolgten sowohl im Sammelurin als auch im 2. Morgenurin und wur- den auf mmol Kreatinin bezogen. NTx-, DPD- und CTx- Bestimmungen wurden bei 28 Patientinnen mit Nieren-, Bronchial- oder Mammakarzinomen parallel zur Knochens- zintigraphie im 2. Morgenurin durchgeführt.
DPD (frei): Pyrilinks-D - EIA (Fa. DPC); NTx: Osteo- mark - EIA (Fa. Ortho Diagnostic Systems); CTx: a-Cross- laps (Fa. Hybritech)
Ergebnisse:
Tabellarische Darstellung der intraindividuellen Varianz (s%):
s%DPD s%NTx s%CTx Sam- Mor- Sam- Mor- Sarn^ Mor- meWU. gen-U. mel-U. gen-U. rriel-U. gen-U.
Mediän 20 Min 5 Max 72
21.57 29 6410
287 68
n.b. 28
1181
Tabellarische Übersicht der absoluten Meßergebnisse im 2. Morgenurin:
DPD NTx ' CTx Kontr-Gr. Karz.-Gr. Kontr-Gr. Karz.-Gr, Kontr.-Gr. Karz.-Gr.
Mediän 5.67 Min 1.31 Max 14.8
8.441.03 139
35,86.76 137
70.620.1 183
231 380 13.4 104 678 4047
Schlußfolgerungen: Mittels der DPD (freie)-, NTx- und CTx-Messungen im Urin sind reproduzierbare Ergebnisse innerhalb der 5 Zyklen nachzuweisen. Somit kann ein sub-
stantieller Knochenabbau gleichermaßen erfaßt werden. Die Bestimmungen der freien DPD zeigen eine geringere intra- individuelle Streuung als die vergleichbaren Ausscheidun- gen von NTx und CTx. Alle Marker gestatten eine gute Dif- ferenzierung zwischen Kontroll- und Karzinomgruppe. Der leichter zu gewinnende 2. Morgenurin ermöglicht vergleich- bare Ergebnisse mit dem Sammelurin.
Literatur
1. Robins SP, Seibel J. Biochemical markers of bone metabolism:
a critical evaluation. Clin Lab 1995;41:987-9.
C-2
Relationship among quantitative ultrasound measurement, serum bone sialoprotein concentrations, and other bone turnover markers in patients with and without hormone replacement therapy W. Withold*, G. Kruempelbeck**, S. Koenig**, M. Karmatschek***, F.R Armbruster***, M.W. Beckmann**
* Institute for Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Diagnostics, University of Duesseldorf
** Clinic for Gynecology, University of Duesseldorf
*** Immundiagnostik GmbH, Bensheim, Germany
Bone sialoprotein, a protein synthesized by osteoblasts and osteoclasts, constitutes a predpminant fraction of non-col- lagenous matrix in bone. Therefore it has been proposed äs a marker of bone turnover. Here we report an assessment of the serum levels of bone sialoprotein in patients with and without hormone replacement therapy, relating the values to those of quantitative ultrasound measurement and other bone turnover markers.
We examined six groups of females (n = 239): (a) Ap- parently healthy women (age < 50 years). (b) Apparently healthy women (age > 50). (c) Patients with different gyne- cological or other diseases either related or not to bone me- tabolism who were divided according to age and presence of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) (c\: age < 50, HRT; c2: age > 50, HRT; c3: age < 50, no HRT; c4: age > 50, no HRT).
Results of ultrasound measurements of the calcanei (Lunar GmbH, Bad Nauheim, Germany) are given in terms of T score values of the "stiffness" (äs compared to a pre- menopausal reference collective).
The following analytes were determined: (a) Serum bone sialoprotein (Immundiagnostik GmbH, Bensheim, Ger- many). (b) Serum bone alkaline phosphatase activity (Alkphase-B), (c) Serum osteocalcin (ELSA-OSTEO). (d) Urinary deoxypyridinoline (Pyrilinks-D). (e) Urinary N-ter- minal telopeptide of Collagen type I (Osteomark).
There was a relalionship between serum bone sialopro- tein on the one hand and bone alkaline phosphatase activity (group C2), osteocalcin (groups b and C|) and N-telopeptide (groups Cj and c3) on the other (p < 0.05). However, no cor- relation could be found between serum bone sialoprotein and T score values in any of the subject groups examined in
contrast lo an inversc relationship between ultrasound mea- surcmcnts and N-telopeptide cxcrclion (p < 0.05).
It is concludcd (hat serum bonc sialoprotcin reflects bone formalion and bonc resorption. Howcvcr, clinica) validity of scrum bone sialoprotein for prcdicting bone mass loss re- quircs furthcr cvalualion.
vers mit der Knochendichte am Femurhals (r = - 0,389; p <
0,01).
Wir sehen aufgrund dieser Ergebnisse die Bestimmung von Pyridinolin im Serum und Dialysat als vielverspechen- de Methode zur Erfassung des Knochenstoffwechsels bei CAPD-Paticnten an.
C-3
Bestimmung von immunreaktivem Pyridinolin im Serum und Dialysat bei Patienten unter chronischer ambulanter Peritonealdialyse: Beziehung zur
Knochenmasse und anderen Kenngrößen des Knochenstoffwechsels
W. Withold*. N. Pausner**, B. Grabensee**
• Institut für Klinische Chemie und Laboratoriumsdiagnostik,
** Klinik für Nephrologie, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Die renale Osteopathie ist bei Patienten mit chronischer Nie- reninsuffizienz eine der schwerwiegendsten Komplikatio- nen. Als Marker-Substanz der Wahl zur Beurteilung der Knochenresorption dient die Urin-Ausscheidung der „pyri- dinium cross-links" (Pyridinolin, Desoxypyridinolin). Da niereninsuffiziente Patienten vielfach oligo- bzw. anurisch sind, haben wir eine Methode zur Bestimmung von immun- reaktivem Pyridinolin im Serum und Dialysat ausgearbeitet.
Wir untersuchten 64 Patienten mit terminal-chronischer Niereninsuffizienz unter chronischer ambulanter Peritoneal- dialyse (23 Frauen und 41 Männer; Alter: 44+11 Jahre; Pe- ritonealdialyse-Dauer: 705 + 789 Tage), hiervon 36 Patien- ten mit Oligo-Anurie. Die Bestimmung von Pyridinolin im Serum und Dialysat erfolgte mittels Pyrilinks-Il™ (Metra Biosystems). Die Zahl der pro 24 h entnommenen Dialysat- Proben betrug 5. Alle Pyridinolin-Werte im Serum und Dia- lysat wurden auf die jeweilige Kreatinin-Konzentration be- zogen.
Routinemäßig erfolgte bei den CAPD-Patienten die Be- stimmung von ionisiertem Calcium, Calcitriol, Parathormon and alkalischer Knochenphosphatase. Die Knochendichte wurde mittels DEXA gemessen.
Die Aufstocküngsversuche im Serum ergaben eine mittle- re Wiederfindungsrate von 96%. Die Intra-Assay-Unpräzi- sion betrug bis zu 8%, die Inter-Assay-Unpräzision bis zu 9%.
In der Dialysat-Flüssigkeit bestand ein zirkadianer Rhy- thmus der Ausscheidung (p < 0,05).
Die Pyridinolin-Konzentration im Serum betrug 60 + 69 /mol Kreatinin, im Dialysat 20 ± 16 /mol, die Urin-Ausscheidung derjenigen Patienten ohne Oligo-Anurie 32 + 29 /mol: Die mittleren Konzentrationen von ioni- siertem Calcium (1,2t mmol/1) und Calcitriol (16 ng/1) lagen an der unteren Grenze des Referenzintervalls, die Messung der Knochendichte ergab erniedrigte Werte (durchschnittlich 90% des Mittelwertes offenbar gesunder Erwachsener [20 - 40 Jahre]). Die Pyridinolin-Konzentration im Dialysat kor- relierte mit derjenigen im Serum (r = + 0,285; p < 0,05), nicht jedoch mit den übrigen o.g. klinisch-chemischen Meß- größen (p > 0,05). Die Pyridinolin-Konzentration im Serum korrelierte mit Parathormon (r = + 0,271; p < 0,05) sowie in-
C-4
Xylosyltransferase: a Biochemical Marker of the Sclerotic Process in Systemic Sclerosis C. Götting*, S. Sollberg**, C: Huerkamp**, J. Kühn*, T. Brinkmann*. T. Krieg**, K. Kleesiek*
* Institut für Laboratoriums- und Transfusionsmedizin, Herz- und Diabeteszentrum Nordrhein-Westfalen, Universitätsklinik der Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen
** Klinik und Poliklinik für Dermatologie und Venerologie, Universität Köln
UDP-D-xylose:proteoglycan core protein ß-D-xylosyltrans- ferase (XT) is the initial enzyme in the biosynthesis of chon- droitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate proteoglycans. Secretion of xylosyltransferase into extracellular space was deter- mined in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. A more than 6- fold accumulation of XT activity in cell culture supernatant was observed (day 1: 0.65 /106 cells, day 9: 4.06 /106
cells). However, intracellular XT activity remained at a con- stant level (0.36 U/l O6 cells). Exposure of human chondro- cytes to colchicine for 24 hours lead to a 3-fold decreased level of XT and chondroitin-6-sulfate concentration in cell culture. XT activity and chondroitin-6-sulfate concentration decreased dose-dependently and in parallel in culture medi- um and accumulated 5-fold in cell lysates indicating that XT is secreted simultaneously into the extracellular space with chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans.
Xylosyltransferase activities were determined in serum samples of 33 patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) [1], XT activities in female (mean value 1.26 mU/1, ränge 1.0-1.53 mU/1) and male patients (mean value 1.42 mU/1, ränge 1. - .57 mU/1) were significantly increased in comparison to blood donors of corresponding age (mean value 0.89, ränge 0.6-1.1 mU/1). Furthermore, XT activity was correlated with the clinical severity of systemic sclerosis. Female patients with·diffuse SSc showed higher serum XT activities (mean value 1.37 mU/l) than patients with limited SSc (mean value 1.16 mU/1). These results confirm that the increase of pro- teoglycan biosynthesis in sclerotic processes of scleroderma is closely related to an elevated XT activity in blood.
Reference
1. Götting C, Sollberg S, Kühn J, Weilke C, Huerkamp C, Brink- mann T, Krieg T, Kleesiek K. Serum Xylosyltransferase: a new Biochemical Marker of the Sclerotic Process in Scleroderma. J In- vest Dermatol (submitted)
C-5
Glycosylation of Alzheimer APP Isoforms by Xylosyltransferase
C. Götting*, J. Kühn*, T. Brinkmann*. "K. Kleesiek*
* Institut für Laboratoriums- und Transfusionsmedizin, Herz- und' f
Diabeteszentrum Nordrhein-Westfalen, Universitätsklinik der Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen
Alzheimer's disease is' a common form of dementia patho- logically characterized by the presence of amyloid deposits.
These plaques comprise the ß-A4-amyloid protein, a prote- olytic fragment of the ß-A4-amyloid protein precursor (APP). APP belongs to a family of related proteins that in- cludes amyloid precursor-like proteins (APLP). Several iso- forms of APP and APLP2 that are generated by alternative splicing of RNA transcripts have been reported (L-APP, L- APLP2). Omission of exon 15 in the L-APP transcripts and of the 12aa exon in L-APLP2 transcripts gbnerates a fusion sequence (ENEGSG) in both proteins that functions äs a po- tential recognition site of xylosyltransferase mediated addi- tion of glycosaminoglycans.
Acceptor affinities of xylosyltransferase (XT) recognition Signals in synthetic L-APP and L-APLP2 homologous pep- tides were determined (1). The Michaelis-Menten constants (KM) of the synthetic L-APP peptide TENEGSGLTNIK and the L-APLP2 peptide SENEGSGMAEQK were 20.1 and 18.9 respectively. Therefore, the peptides proved to be äs good acceptors for XT äs the bikunin aminoterminus homologous peptide (KM=22 ). Due to occurence of L-APP and L-APLP2 transcripts in human brain tissue XT activity was rneasured in liquor cerebrospinalis. Mean val- ues were calculated äs 0.22 mU/1 in males and 0.47 mU/1 in females without disturbance of blood-brain-barrier. In addi- tion in homogenized rat brain tissue a mean XT activity of 0.75 mU/1 was determined. Furthermore, XT activity was in- vestigated in 21 different human cell lines. In 7 cell lines an enzyme activity was not detected, in either extracellular space or cytoplasma.
Reference
1. Götting C, Kühn J, Brinkmann T, Kleesiek K. Xylosylation of Alternatively Spliced Isoforms of Alzheimer APP by Xylosyltrans- ferase. J Prot Chem 1998;17:295-302.
C-6
Platelet Derived Growth Factors Stimulate Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Synthesis of Fat Storing Pancreatic Stellate Cells: Implications in Pathogenesis of Chronic Pancreatitis
T. Luttenberger*, E. Schneider*, HJ. Gross*,
A. Schmid-Kotsas*, A. Grünert*, A. Menke**, G. Adler*, M. Siech***, M.G. Bachern*
* Dept. of Clinical Chemistry
** Dept. of Medicine l
*** Dept. of Surgery, University Hospital, Ulm, Germany
Recently we have identified and characterized stellate cells (PSC) in rat and human pancreas and suggested a prominent role of these cells in chronic pancreatitis [l]. In this study we investigated the effects of platelet derived growth factors on extracellular matrix synthesis and cell proliferation of cultured human PSC.
Methods and results: Human PSC were isolated from his- tologically fibrotic areas of the pancreas. Cells were cultured in DMEM/HAMs F12 and used between passage 4-7. Na- tive and transiently acidified platelet lysate (30, 60, 90 and 120 /ml medium) were added to cultured PSC. As shown by immunofluorescence, quantitative immunoassay and northern-blot analysis, the synthesis of c-fibronectin and collagen type I was increased dose dependently by native platelet lysate and to an even higher extent by transiently acidified platelet lysate. Furthermore platelet lysate signifi- cantly stimulated cell proliferation measured by bromod- eoxyuridine incorporation and fluorometric DNA determina- tion (native platelet lysate caused a 6.4-fold, acidified platelet lysate a 10-fold stimulated BrdU incorporation). To identify the stimulating mediators the grpwth factors bFGF, PDGF(AB), TGFa, IGFs (all 20 ng/ml) and TGFßl (2 ng/ml) were added alone and in combination to cultured human PSCs. In particular PDGF stimulated cell prolifera- tion and bFGF and TGFßl stimulated matrix synthesis.
Summary: Our data strongly suggest that platelets and PSC cooperate in the development of pancreas fibrosis. Dur- ing aggregation platelets release growth factors which stim- ulate proliferation and matrix synthesis of PSC.
Reference
1. Bachern MG et al. Gastroenterology 1998;! 15:421-35.