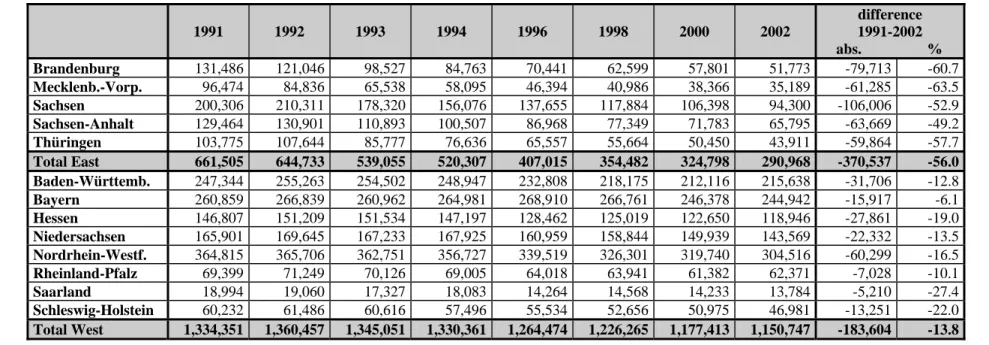
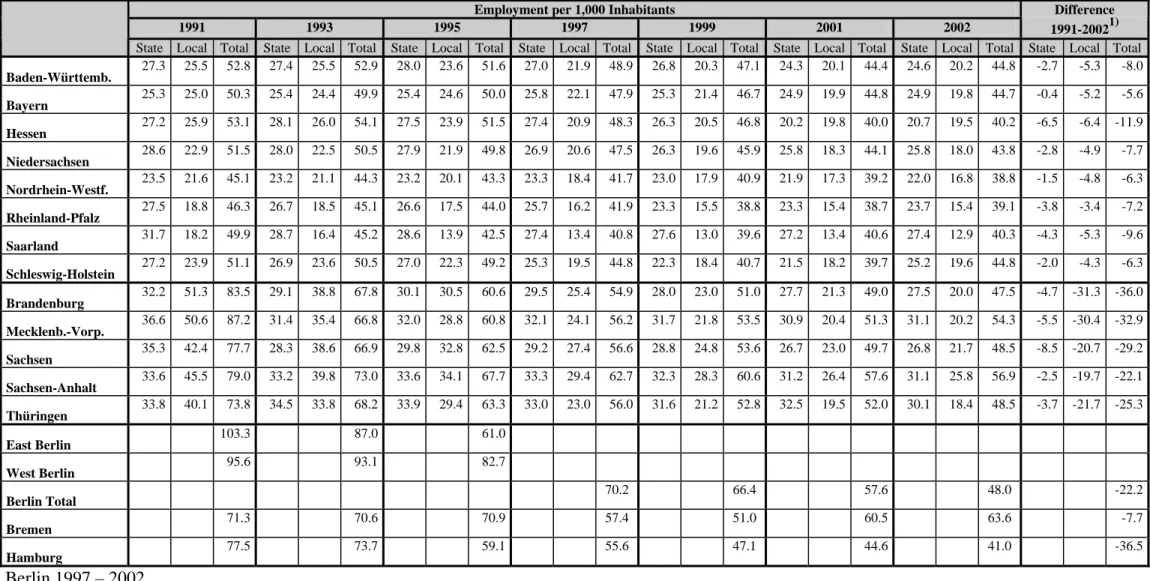
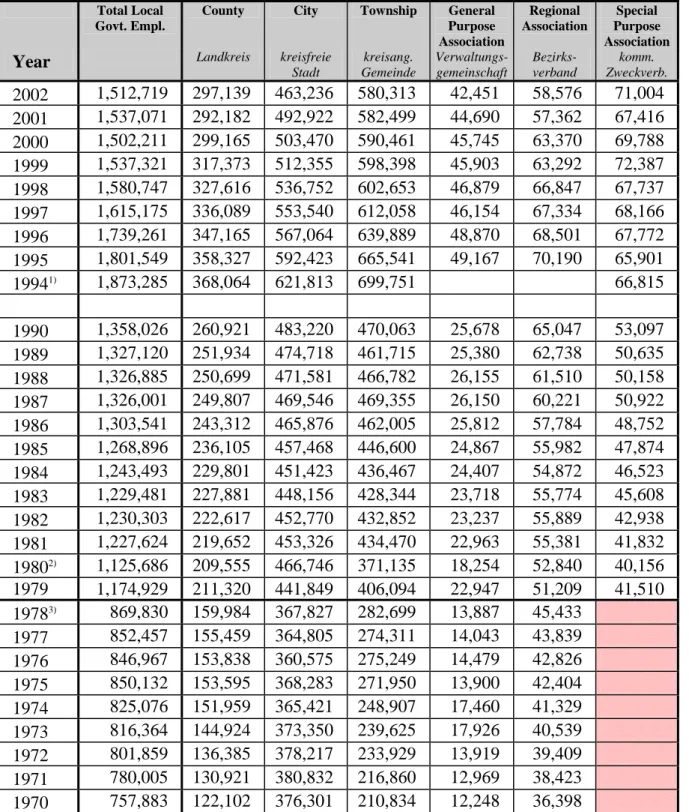
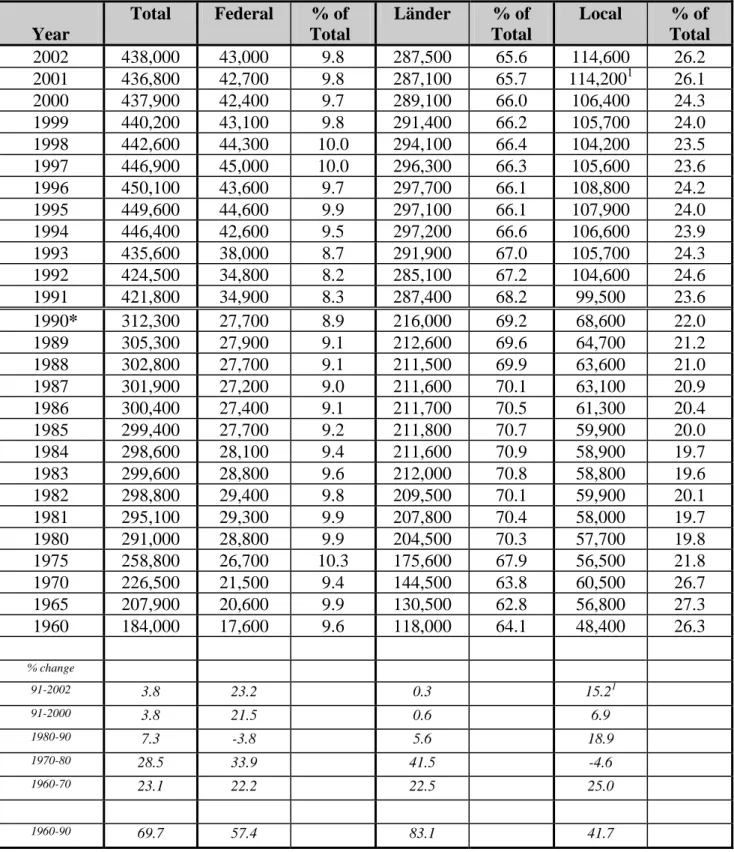
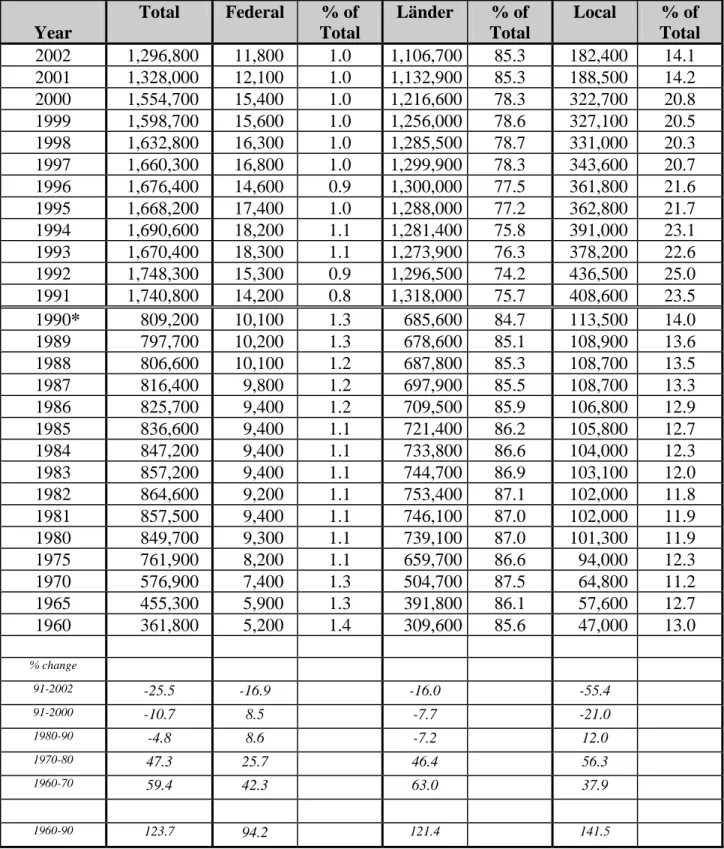
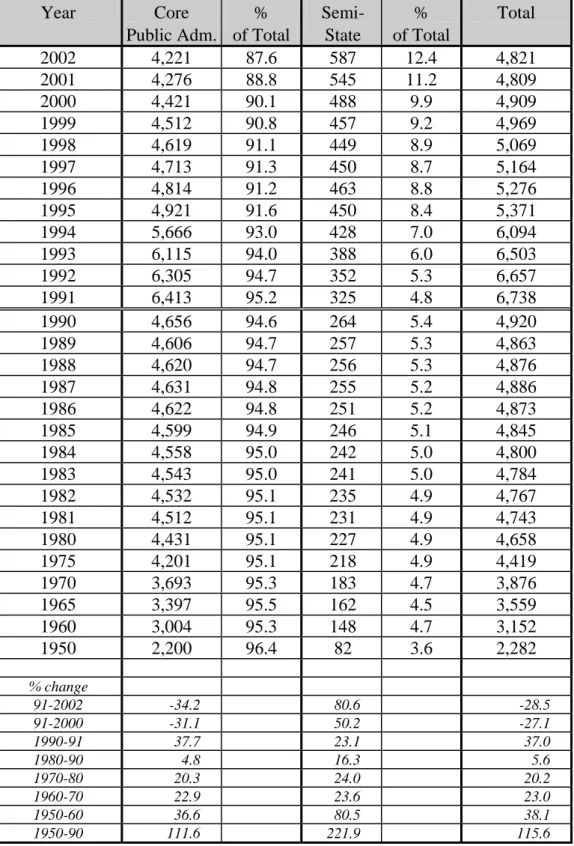
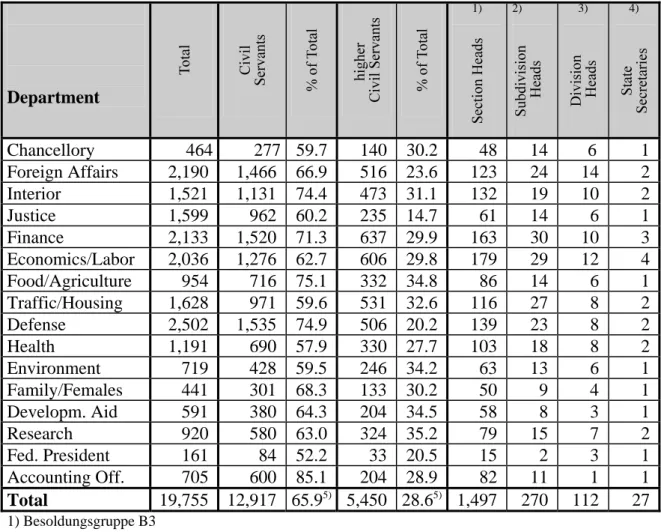
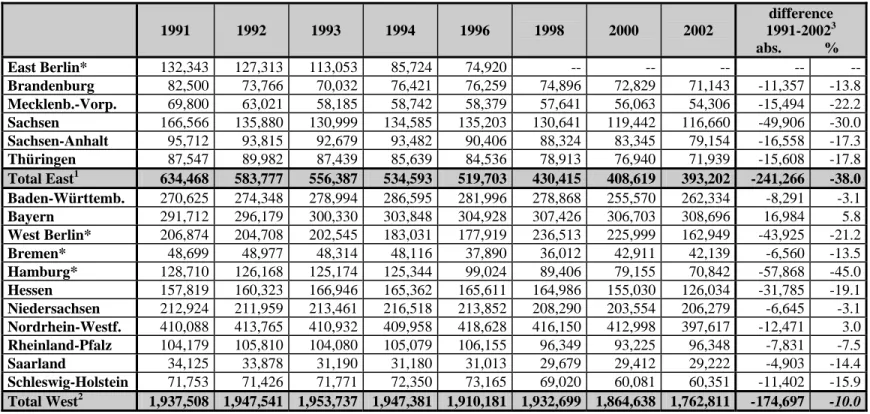
THE GERMAN PUBLIC SERVICE - STRUCTURE AND STATISTICS
Volltext
Abbildung

ÄHNLICHE DOKUMENTE
These shifts in the local conceptions of crime, in the conception of citizenship and in the conception of the legitimacy of state violence are embedded in global
This paper considers corruption in higher education as a product of interrelations between the government and academia and argues that suppressed university autonomy is used by the
The point is that only the human sciences are entangled with normativity in a special and much more far-reaching way, namely simply because only the human sciences deal
According to Alejandro Quiroz Flores, the modern state holds two comparative advantages over other forms of political organization — it is far better at directing large and
China has used the move as a pretext to challenge Japanese administration of the islands by deploying ships and aircraft to patrol the adjacent waters.. In a departure from
Together, these two conditions – the advance of technology due to international anarchy and the Hegelian struggle towards symmetrical recognition – make a world state
We exploit the fact that the economies of medieval and early modern Europe were predominantly agrarian and use exogenous variation in temperature during the growing season to
In the history of political and economic culture of the world, facts have suggested that, while considering the relevant issues, intellectual effect can very well prevent the